Page 176 - IJOCTA-15-4
P. 176
Oleiwi et al. / IJOCTA, Vol.15, No.4, pp.706-727 (2025)
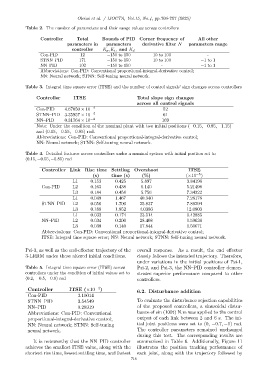
Table 2. The number of parameters and their range values across controllers
Controller Total Bounds of PID Corner frequency of All other
parameters in parameters derivative filter N parameters range
controller K p , K i , and K d
Con-PID 12 −150 to 150 10 to 100 -
STNN–PID 171 −150 to 150 10 to 100 −1 to 1
NN–PID 102 −150 to 150 - −1 to 1
Abbreviations: Con-PID: Conventional proportional-integral-derivative control;
NN: Neural network; STNN: Self-tuning neural network.
Table 3. Integral time square error (ITSE) and the number of control signals’ sign changes across controllers
Controller ITSE Total slope sign changes
across all control signals
Con-PID 4.67050 × 10 −4 52
STNN–PID 3.35957 × 10 −4 61
NN–PID 0.31764 × 10 −4 169
Note: Under the condition of the nominal plant with two initial positions (−0.15, −0.85, −1.15)
and (0.15, −0.55, −0.85) rad.
Abbreviations: Con-PID: Conventional proportional-integral-derivative control;
NN: Neural network; STNN: Self-tuning neural network.
Table 4. Detailed features across controllers under a nominal system with initial position set to
(0.15, −0.55, −0.85) rad
Controller Link Rise time Settling Overshoot ITSE
(s) time (s) (%) (×10 −5 )
L1 0.153 0.425 5.897 3.84196
Con-PID L2 0.163 0.438 6.140 5.21498
L3 0.184 0.458 5.756 7.34322
L1 0.049 1.467 40.940 7.26176
STNN–PID L2 0.050 1.700 25.837 7.86294
L3 0.188 1.852 4.0386 12.0803
L1 0.032 0.174 23.514 0.42885
NN–PID L2 0.034 0.200 28.408 0.59636
L3 0.039 0.140 17.844 0.50671
Abbreviations: Con-PID: Conventional proportional-integral-derivative control;
ITSE: Integral time square error; NN: Neural network; STNN: Self-tuning neural network.
Psi-3, as well as the end-effector trajectory of the overall response. As a result, the end effector
3-LRRM under these altered initial conditions. closely follows the intended trajectory. Therefore,
under variations in the initial positions of Psi-1,
Table 5. Integral time square error (ITSE) across Psi-2, and Psi-3, the NN–PID controller demon-
controllers under the condition of initial values set to strates superior performance compared to other
(0.2, −0.5, −0.8) rad controllers.
Controller ITSE (×10 −4 )
6.2. Disturbance addition
Con-PID 3.10014
STNN–PID 3.54549 To evaluate the disturbance rejection capabilities
NN–PID 0.28919 of the proposed controllers, a sinusoidal distur-
Abbreviations: Con-PID: Conventional bance of sin (100t) N.m was applied to the control
proportional-integral-derivative control; output of each link between 2 and 6 s. The ini-
NN: Neural network; STNN: Self-tuning tial joint positions were set to (0, −0.7, −1) rad.
neural network. The controller parameters remained unchanged
during this test. The corresponding results are
It is noteworthy that the NN–PID controller summarized in Table 6. Additionally, Figure 11
achieves the smallest ITSE value, along with the illustrates the position tracking performance of
shortest rise time, lowest settling time, and fastest each joint, along with the trajectory followed by
718