Page 87 - IJPS-11-1
P. 87
International Journal of
Population Studies Cultural values and workplace gender equity
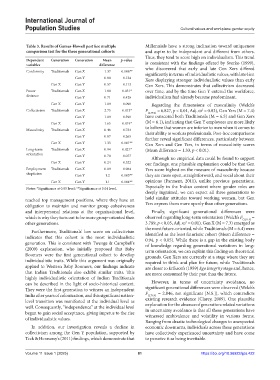
Table 3. Results of Games‑Howell post hoc multiple Millennials have a strong inclination toward uniqueness
comparison test for the three generational cohorts and aspire to be independent and different from others.
Thus, they tend to score high on individualism. This trend
Dependent Generation Generation Mean p‑value
variables difference is consistent with the findings offered by Sverko (1999),
Conformity Traditionals Gen X 1.37 0.006** who discovered that early and late Gen Xers differed
significantly in terms of individualistic values, with late Gen
Gen Y 0.80 0.124 Xers displaying stronger individualistic values than early
Gen X Gen Y 0.57 0.113 Gen Xers. This demonstrates that collectivism decreased
Power Traditionals Gen X 1.80 0.031* over time, and by the time Gen Y entered the workforce,
distance Gen Y 0.71 0.426 individualism had already become predominant.
Gen X Gen Y 1.09 0.090 Regarding the dimensions of masculinity (Welch’s
Collectivism Traditionals Gen X 2.75 0.013* F (2,79.2) = 6.827, p < 0.01, Adj. ω = 0.03), Gen Yers (M = 7.4)
2
Gen Y 1.09 0.390 have outscored both Traditionals (M = 6.5) and Gen Xers
Gen X Gen Y 1.65 0.019* (M = 6.1), indicating that Gen Y employees are more likely
Masculinity Traditionals Gen X 0.46 0.724 to believe that women are inferior to men when it comes to
their ability to work as professionals. Post-hoc comparisons
Gen Y 0.87 0.265
further reveal significant differences, particularly between
Gen X Gen Y 1.33 0.001** Gen Xers and Gen Yers, in terms of masculinity scores
Long-term Traditionals Gen X 0.94 0.021* (Mean difference = 1.33, p < 0.01).
orientation Gen Y 0.70 0.077 Although no empirical data could be found to support
Gen X Gen Y 0.24 0.522 our findings, one plausible explanation could be that Gen
Employment Traditionals Gen X 0.09 0.984 Yers score highest on the measure of masculinity because
skepticism Gen Y 1.2 0.003** they are more open, straightforward, and vocal about their
Gen X Gen Y 1.1 0.004** opinions (Parment, 2011), unlike previous generations.
Notes: *Significance at 0.05 level; **Significance at 0.01 level. Especially in the Indian context where gender roles are
deeply ingrained, we can expect all three generations to
reached top management positions, where they have an hold similar attitudes toward working women, but Gen
obligation to maintain and monitor group cohesiveness Yers express them more openly than other generations.
and interpersonal relations at the organizational level, Finally, significant generational differences were
which is why they turn out to be more group-oriented than observed regarding long-term orientation (Welch’s F (2,81.4) =
other generations. 3.789, p < 0.05, Adj. ω = 0.01). Gen X (M = 7.3) emerged as
2
the most future-oriented, while Traditionals (M = 6.4) were
Furthermore, Traditionals’ low score on collectivism identified as the least futuristic cohort (Mean difference =
indicates that this cohort is the most individualistic 0.94, p < 0.05). While there is a gap in the existing body
generation. This is consistent with Twenge & Campbell’s of knowledge regarding generational variations in long-
(2009) explanation, who initially proposed that Baby term orientation, we can explain this finding on theoretical
Boomers were the first generational cohort to develop grounds. Gen Xers are currently at a stage where they are
individualistic traits. While this argument was originally required to think and plan for future, while Traditionals
applied to Western Baby Boomers, our findings indicate are closer to Erikson’s (1959) Ego Integrity stage and, hence,
that Indian Traditionals also exhibit similar traits. This are more consumed by their past than the future.
highly individualistic orientation of Indian Traditionals
can be described in the light of socio-historical context. However, in terms of uncertainty avoidance, no
They were the first generation to witness an independent significant generational differences were observed (Welch’s
India after years of colonization, and this significant nation- F (2,76.4) = 2.846, not significant [N.S.]), which contradicts
level transition was manifested at the individual level as existing research evidence (Clarey, 2009). One plausible
well. Consequently, “independence” at the individual level explanation for the absence of generation-related variations
began to gain social acceptance, giving impetus to the rise in uncertainty avoidance is that all these generations have
of individualistic values. witnessed ambivalence and volatility in various forms.
Ranging from drastic technological changes to unexpected
In addition, our investigation reveals a decline in economic downturns, individuals across these generations
collectivism among the Gen Y population, supported by have collectively experienced uncertainty and have come
Teck & Hennessy’s (2011) findings, which demonstrate that to perceive it as being inevitable.
Volume 11 Issue 1 (2025) 81 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijps.422