Page 117 - ITPS-7-1
P. 117
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences Repurposed Drugs as inhibitors of Pfmrk
Plasmodium ovale, and Plasmodium malariae. Among substrate of Pfmrk . While it has been demonstrated that
[5]
these, P. falciparum is associated with the most severe and plasmodial CDKs can be inhibited by mammalian CDK
potentially fatal cases of malaria. According to the World inhibitors , the existence of CDK inhibitory proteins in
[6]
Health Organization (WHO), a staggering 300 – 500 million Plasmodium remains undiscovered. Therefore, Pfmrk holds
malaria cases are reported annually, with the majority of promise as a drug target in antimalarial drug screening.
these cases occurring in Africa. High prevalence is also In the present study, we have leveraged this foundational
observed in regions such as India, Sri Lanka, Thailand, knowledge to determine the potential of selected drugs to
Indonesia, Vietnam, China, and Cambodia. In addition, interact with and potentially inhibit the Pfmrk protein.
malaria claims the lives of more than 2 million individuals The extensive molecular docking and simulation study
each year .
[2]
identified two promising candidate drugs. These drugs
The parasite’s complex life cycle involves plasmodial warrant further investigation in in vitro studies, with the
cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) and cyclin proteins for aim of their potential addition to drug panels for malaria
its persistence in both vertebrate and invertebrate hosts . treatment in the future.
[3]
These proteins play essential roles in the parasite’s survival,
both extracellularly and intracellularly. Plasmodial CDKs, 2. Materials and methods
such as Pfmrk, belong to the Apicomplex, a specific protein 2.1. Sequence homology between Pfmrk and hCDK7
kinase subfamily analogous to CDKs. Pfmrk, akin to CDK7,
functions as an upstream kinase, facilitating the activation Sequence homology between Pfmrk and hCDK7 was
of multiple CDKs during a cell cycle . It is also known as assessed through multiple sequence alignment, employing
[4]
a CDK-activating kinase due to this role. Pfmrk activates the Clustal Omega (1.2.4) tool (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/
Cdkl, Cdk2, Cdk3, Cdk4, and Cdk6 by activating the Tools/msa/clustalo/). The Fast Amino Acid Sequence
C-terminal domain (CTD) of RNA polymerase II through Search Tool (FASTA) sequence of Pfmrk (ID: P90584)
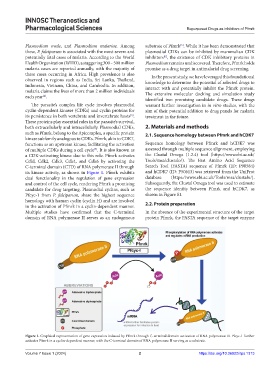
its kinase activity, as shown in Figure 1. Pfmrk exhibits and hCDK7 (ID: P50613) was retrieved from the UniProt
dual functionality in the regulation of gene expression database (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/clustalo/).
and control of the cell cycle, rendering Pfmrk a promising Subsequently, the Clustal Omega tool was used to estimate
candidate for drug targeting. Plasmodial cyclins, such as the sequence identity between Pfmrk and hCDK7, as
Pfcyc-1 from P. falciparum, share the highest sequence shown in Figure S1.
homology with human cyclin (cyclin H) and are involved
in the activation of Pfmrk in a cyclin-dependent manner. 2.2. Protein preparation
Multiple studies have confirmed that the C-terminal In the absence of the experimental structure of the target
domain of RNA polymerase II serves as an endogenous protein Pfmrk, the FASTA sequence of the target enzyme
Figure 1. Graphical representation of gene expression induced by Pfmrk through C-terminal domain activation of RNA polymerase II. Pfcyc-1 further
activates Pfmrk in a cyclin-dependent manner, with the C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II serving as a substrate.
Volume 7 Issue 1 (2024) 2 https://doi.org/10.36922/itps.1313