Page 120 - ITPS-7-1
P. 120
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences Repurposed Drugs as inhibitors of Pfmrk
A B C
D E
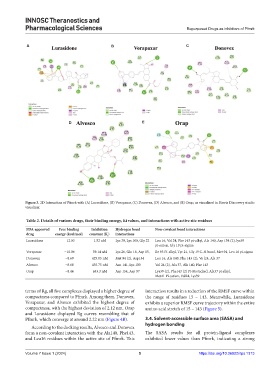
Figure 3. 2D Interaction of Pfmrk with (A) Lurasidone, (B) Vorapaxar, (C) Donovex, (D) Alvesco, and (E) Orap, as visualized in Biovia Discovery studio
visualizer.
Table 2. Details of various drugs, their binding energy, Ki values, and interactions with active site residues
FDA‑approved Free binding Inhibition Hydrogen bond Non‑covalent bond interactions
drug energy (kcal/mol) constant (K ) interactions
i
Lurasidone −12.03 1.52 nM Lys 39, Lys 100, Gly 22 Leu 16, Val 24, Phe 143 pi-alkyl, Ala 140, Asp 154 (2), lys39
pi-anion, Gly 19 pi-sigma
Vorapaxar −10.06 39.14 nM Lys 26, Glu 18, Asp 15, Ile 93 Pi-alkyl, Tyr 21, Gly 19 C-H bond, Met 94, Leu 16 pi-sigma
Donovex −8.69 429.05 nM Met 94 (2), Asp154 Leu 16, Ala 140, Phe 143 (2), Va l24, Ala 37
Alvesco −8.68 435.75 nM Asn 141, Lys 100 Val 24 (2), Ala 37, Ala 140, Phe 143
Orap −8.46 633.3 nM Asp 154, Asp 97 Lys39 (2), Phe143 (2) Pi-Pi stacked, Ala37 pi alkyl,
Met41 Pi cation, Val24, Lys39
terms of Rg, all five complexes displayed a higher degree of interaction results in a reduction of the RMSF curve within
compactness compared to Pfmrk. Among them, Donovex, the range of residues 15 – 143. Meanwhile, Lurasidone
Vorapaxar, and Alvesco exhibited the highest degree of exhibits a superior RMSF curve trajectory within the entire
compactness, with the highest deviation of 2.12 nm. Orap amino acid stretch of 15 – 143 (Figure 5).
and Lurasidone displayed Rg curves resembling that of
Pfmrk, which converge at around 2.22 nm (Figure 4B). 3.4. Solvent-accessible surface area (SASA) and
hydrogen bonding
According to the docking results, Alvesco and Donovex
form a non-covalent interaction with the Ala140, Phe143, The SASA results for all protein-ligand complexes
and Leu16 residues within the active site of Pfmrk. This exhibited lower values than Pfmrk, indicating a strong
Volume 7 Issue 1 (2024) 5 https://doi.org/10.36922/itps.1313