Page 123 - ITPS-7-1
P. 123
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences Repurposed Drugs as inhibitors of Pfmrk
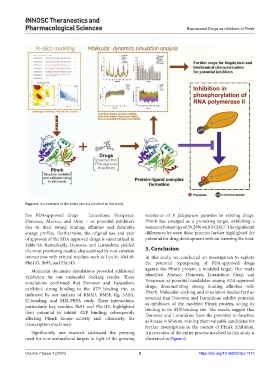
Figure 6. An overview of the entire process involved in this study.
five FDA-approved drugs – Lurasidone, Vorapaxar, resistance of P. falciparum parasites to existing drugs.
Donovex, Alvesco, and Orap – as potential inhibitors Pfmrk has emerged as a promising target, exhibiting a
due to their strong binding affinities and favorable sequence homology of 36.28% with hCDK7. The significant
energy profiles. Furthermore, the original use and year differences between these proteins further highlighted the
of approval of the FDA-approved drugs is summarized in potential for drug development without harming the host.
Table S4. Remarkably, Donovex and Lurasidone yielded
the most promising results, characterized by non-covalent 5. Conclusion
interactions with critical residues such as Leu16, Ala140, In this study, we conducted an investigation to explore
Phe143, Ile93, and Phe143. the potential repurposing of FDA-approved drugs
Molecular dynamics simulations provided additional against the Pfmrk protein, a modeled target. Our study
validation for our molecular docking results. These identified Alvesco, Donovex, Lurasidone, Orap, and
simulations confirmed that Donovex and Lurasidone Vorapaxar as potential candidates among FDA-approved
exhibited strong binding to the ATP binding site, as drugs, demonstrating strong binding affinities with
indicated by our analysis of RMSD, RMSF, Rg, SASA, Pfmrk. Molecular docking and simulation studies further
revealed that Donovex and Lurasidone exhibit potential
H-bonding, and MM-PBSA study. These interactions,
particularly key residues Ile93 and Phe143, highlighted as inhibitors of the modeled Pfmrk protein, acting by
binding to its ATP-binding site. The results suggest that
their potential to inhibit ATP binding, subsequently Donovex and Lurasidone have the potential to function
affecting Pfmrk kinase activity and, ultimately, the as kinase inhibitors, making them valuable candidates for
transcription machinery. further investigation in the context of Pfmrk inhibition.
Significantly, our research addressed the pressing An overview of the entire process involved in this study is
need for new antimalarial targets in light of the growing illustrated in Figure 6.
Volume 7 Issue 1 (2024) 8 https://doi.org/10.36922/itps.1313