Page 75 - ITPS-7-1
P. 75
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences Docking study of quinoline-3-carbaldehyde derives
A
A
B
B
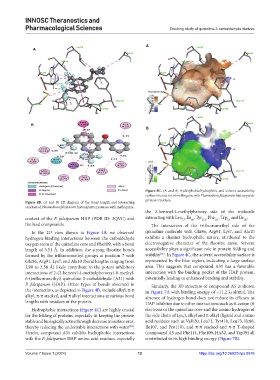
Figure 8C. (A and B) Hydrophobic/hydrophilic and solvent accessibility
surface interaction of mefloquine with Plasmodium falciparum histoaspartic
protease residues.
Figure 8B. (A and B) 2D diagram of the bond length and interacting
residues of Plasmodium falciparum histoaspartic protease with mefloquine.
the 2-benzoyl-4-methylphenoxy side of the molecule
context of the P. falciparum HAP (PDB ID: 3QVC) and interacting with Leu , Ile , Tyr , Phe , Trp and Ile .
80
112
111
39,
107
73
the lead compounds. The interaction of the trifluoromethyl side of the
In the 2D view shown in Figure 4B, we observed quinoline molecule with Glu86, Arg91, Lys7, and Ala10
hydrogen-binding interactions between the carbaldehyde exhibits a distinct hydrophilic nature, attributed to the
oxygen atom of the quinoline core and Phe109, with a bond electronegative character of the fluorine atom. Solvent
length of 3.51 Å. In addition, the strong fluorine bonds accessibility plays a significant role in protein folding and
[35]
formed by the trifluoromethyl groups at position 7 with stability . In Figure 4C, the solvent accessibility surface is
Glu86, Arg91, Lys7, and Ala10 (bond lengths ranging from represented by the blue region, indicating a large surface
2.98 to 3.58 Å) likely contribute to the potent inhibitory area. This suggests that compound A31 has a favorable
interactions of 2-(2-benzoyl-4-methylphenoxy)-8-methyl- interaction with the binding pocket of the HAP protein,
6-(trifluoromethyl) quinoline-3-carbaldehyde (A31) with potentially leading to enhanced binding and stability.
P. falciparum (HAP). Other types of bonds observed in Similarly, the 3D structure of compound A5 is shown
the interaction, as depicted in Figure 4B, include alkyl, π-π in Figure 7A with binding energy of −11.2 kcal/mol. The
alkyl, π-π stacked, and π alkyl interactions at various bond absence of hydrogen bond does not reduce its efficacy as
lengths with residues of the protein. HAP inhibitor due to other interactions such as π-cation (π
Hydrophobic interactions (Figure 4C) are highly crucial electrons of the quinoline core and the amino hydrogen of
for the folding of proteins, especially in keeping the protein the side chain of Lys ), alkyl and π-alkyl (ligand and amino
7
stable and biologically active through decrease in surface area, acid residues such as Val120, Leu73, Tyr410, Leu73, Ile80,
thereby reducing the undesirable interactions with water . Ile107, and Pro110), and π-π stacked and π-π T-shaped
[34]
Herein, compound A31 exhibits hydrophobic interactions (compound A5 and Phe111, Phe109, His32, and Trp39) all
with the P. falciparum HAP amino acid residues, especially contributed to its high binding energy (Figure 7B).
Volume 7 Issue 1 (2024) 12 https://doi.org/10.36922/itps.0976