Page 74 - ITPS-7-1
P. 74
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences Docking study of quinoline-3-carbaldehyde derives
A A
B
B
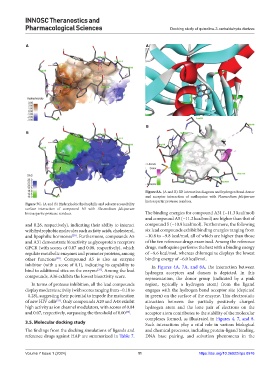
Figure 8A. (A and B) 3D interaction diagram and hydrogen bond donor
and acceptor interaction of mefloquine with Plasmodium falciparum
histoaspartic protease residues.
Figure 7C. (A and B) Hydrophobic/hydrophilic and solvent accessibility
surface interaction of compound A5 with Plasmodium falciparum
histoaspartic protease residues. The binding energies for compound A31 (−11.3 kcal/mol)
and compound A5 (−11.2 kcal/mol) are higher than that of
and 0.26, respectively), indicating their ability to interact compound 5 (−10.9 kcal/mol). Furthermore, the following
with hydrophobic molecules such as fatty acids, cholesterol, six lead compounds exhibit binding energies ranging from
[29]
and lipophilic hormones . Furthermore, compounds A5 −10.8 to −9.8 kcal/mol, all of which are higher than those
and A31 demonstrate bioactivity as glycoprotein receptors of the ten reference drugs examined. Among the reference
GPCR (with scores of 0.07 and 0.08, respectively), which drugs, mefloquine performs the best with a binding energy
regulate metabolic enzymes and promoter proteins, among of −9.6 kcal/mol, whereas chloroquine displays the lowest
other functions . Compound A5 is also an enzyme binding energy of −6.0 kcal/mol.
[30]
inhibitor (with a score of 0.1), indicating its capability to In Figures 4A, 7A, and 8A, the interaction between
bind to additional sites on the enzyme . Among the lead hydrogen acceptors and donors is depicted. In this
[31]
compounds, A36 exhibits the lowest bioactivity score. representation, the donor group (indicated by a pink
In terms of protease inhibition, all the lead compounds region, typically a hydrogen atom) from the ligand
display moderate activity (with scores ranging from −0.18 to engages with the hydrogen bond acceptor site (depicted
−0.28), suggesting their potential to impede the maturation in green) on the surface of the enzyme. This electrostatic
of new HIV cells . Only compounds A20 and A48 exhibit attraction between the partially positively charged
[32]
high activity as ion channel modulators, with scores of 0.04 hydrogen atom and the lone pair of electrons on the
and 0.07, respectively, surpassing the threshold of 0.00 . acceptor atom contributes to the stability of the molecular
[33]
complexes formed, as illustrated in Figures 4, 7, and 8.
3.5. Molecular docking study Such interactions play a vital role in various biological
The findings from the docking simulations of ligands and and chemical processes, including protein-ligand binding,
reference drugs against HAP are summarized in Table 7. DNA base pairing, and solvation phenomena in the
Volume 7 Issue 1 (2024) 11 https://doi.org/10.36922/itps.0976