Page 39 - ITPS-8-2
P. 39
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences MDD biomarkers: Clinical implications
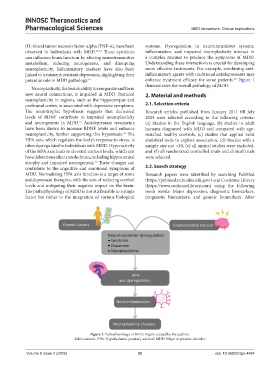
(IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), have been systems. Dysregulation in neurotransmitter systems,
observed in individuals with MDD. 11,13 These cytokines inflammation, and impaired neuroplasticity interact in
can influence brain function by altering neurotransmitter a complex manner to produce the symptoms of MDD.
metabolism, reducing neurogenesis, and disrupting Understanding these interactions is crucial for developing
neuroplasticity. Inflammatory markers have also been more effective treatments. For example, combining anti-
linked to treatment-resistant depression, highlighting their inflammatory agents with traditional antidepressants may
18
potential role in MDD pathology. 14 enhance treatment efficacy for some patients. Figure 1
demonstrates the overall pathology of MDD.
Neuroplasticity, the brain’s ability to reorganize and form
new neural connections, is impaired in MDD. Reduced 2. Material and methods
neuroplasticity in regions, such as the hippocampus and
prefrontal cortex, is associated with depressive symptoms. 2.1. Selection criteria
The neurotrophic hypothesis suggests that decreased Research articles published from January 2011 till July
levels of BDNF contribute to impaired neuroplasticity 2024 were selected according to the following criteria:
and neurogenesis in MDD. Antidepressant treatments (a) Studies in the English language, (b) studies in adult
15
have been shown to increase BDNF levels and enhance humans diagnosed with MDD and compared with age-
neuroplasticity, further supporting this hypothesis. The matched healthy controls, (c) studies that applied valid
16
HPA axis, which regulates the body’s response to stress, is statistical tools to explore association, (d) Studies with a
often dysregulated in individuals with MDD. Hyperactivity sample size not <10, (e) all animal studies were excluded,
of the HPA axis leads to elevated cortisol levels, which can and (f) all randomized controlled trials and clinical trials
have deleterious effects on the brain, including hippocampal were selected.
atrophy and impaired neurogenesis. These changes can
17
contribute to the cognitive and emotional symptoms of 2.2. Search strategy
MDD. Normalizing HPA axis function is a target of some Research papers were identified by searching PubMed
antidepressant therapies, with the aim of reducing cortisol (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/) and Cochrane Library
levels and mitigating their negative impact on the brain. (https://www.cochranelibrary.com) using the following
The pathophysiology of MDD is not attributable to a single mesh words: Major depression, diagnostic biomarkers,
factor but rather to the integration of various biological prognostic biomarkers, and genetic biomarkers. After
Figure 1. Pathophysiology of MDD. Figure created by the authors.
Abbreviations: HPA: Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal; MDD: Major depressive disorder.
Volume 8 Issue 2 (2025) 33 doi: 10.36922/itps.4404