Page 41 - ITPS-8-2
P. 41
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences MDD biomarkers: Clinical implications
Table 1. Summary of cell surface signaling biomarkers in MDD
Biomarker Source/Type Role in MDD Key findings References
TOLLIP Immune cells Inflammation May distinguish MDD patients with childhood abuse 19
VEGF Blood Neurogenesis Potential diagnostic marker for MDD 30
Homocysteine Blood NMDAR agonist Potential biomarker for MDD in acute coronary syndrome patients 20
DHEAS Blood Neurosteroid Treatment response biomarker 21
BDNF Serum Neuroplasticity Predictive biomarker for MDD vulnerability 22
Abbreviations: BDNF: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor; DHEAS: Dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate; MDD: Major depressive disorder;
NMDAR: N-methyl D-aspartate receptors; TOLLIP: Toll-like interacting protein; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor.
depression by stimulating the opening of mitochondrial
permeability transition pores through transcriptional
upregulation of cyclophilin D. Cyclophilin D inhibition
35
using a mitochondria-targeted compound, mito-apocynin,
and a GC receptor antagonist, mifepristone, protects
against mitochondrial dysfunction, synaptic loss, and
behavioral deficits induced by GC. 35
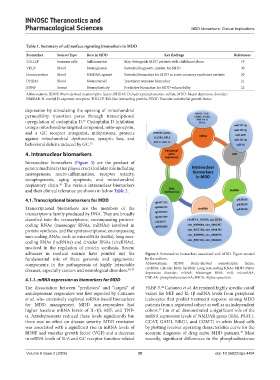
4. Intranuclear biomarkers
Intranuclear biomarkers (Figure 3) are the product of
genetic machinery that plays a crucial cellular role including
neurogenesis, neuro-inflammation, receptor toxicity,
synaptogenesis, aging apoptosis, and mitochondrial
respiratory chain. The various intranuclear biomarkers
36
and their clinical relevance are shown in below Table 2.
4.1. Transcriptional biomarkers for MDD
Transcriptional biomarkers are the members of the
transcriptome family produced by DNA. They are broadly
classified into the transcriptome, encompassing protein-
coding RNAs (messenger RNAs; mRNAs) involved in
protein synthesis, and the epitranscriptome, encompassing
non-coding RNAs, such as microRNAs (miRs), long non-
coding RNAs (lncRNAs) and circular RNAs (circRNAs),
involved in the regulation of protein synthesis. Recent
advances in medical science have pointed out the Figure 3. Intranuclear biomarkers associated with MDD. Figure created
fundamental role of these genomic and epigenomic by the authors.
components in the pathogenesis of highly intractable Abbreviations: BDNF: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor;
diseases, especially cancers and neurological disorders. 42,43 circRNA: Circular RNA; lncRNA: Long non-coding RNAs; MDD: Major
depressive disorder; mRNA: Messenger RNA; miR: microRNA;
4.1.1. mRNA expression as biomarkers for MDD PDE-8A: phosphodiesterase 8A; SNCA: Alpha-synuclein.
The dissociation between “predictors” and “targets” of FKBP-5. Cattaneo et al. determined highly specific cutoff
44
antidepressant responders was first reported by Cattaneo values for MIF and IL-1β mRNA levels from peripheral
et al. who extensively explored mRNA-based biomarkers leukocytes that predict treatment response among MDD
for MDD management. MDD non-responders had patients from a registered cohort as well as an independent
higher baseline mRNA levels of IL-1β, MIF, and TNF- cohort. Lin et at. demonstrated a significant role of the
37
α. Antidepressants reduced these levels significantly but mRNA expression levels of NMDAR genes (SRR, PSAT1,
there was no effect on disease severity. MDD remission GCAT, GAD1, NRG1, and COMT) in white blood cells
was associated with a significant rise in mRNA levels of by plotting receiver operating characteristics curve for the
BDNF and vascular growth factor (VGF) and a decrease accurate diagnosis of drug naïve MDD patients. Most
45
in mRNA levels of IL-6 and GC receptor function-related recently, significant differences in the phosphodiesterase
Volume 8 Issue 2 (2025) 35 doi: 10.36922/itps.4404