Page 70 - ITPS-8-2
P. 70
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences Preclinical study of GBpoietin biosimilar
A C E G
B D F H
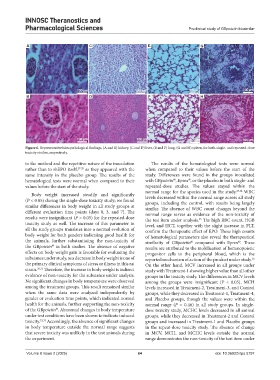
Figure 6. Representative histopathological findings. (A and B) kidney, (C and D) liver, (E and F) lung, (G and H) spleen, for both single- and repeated-dose
toxicity studies, respectively.
to the method and the repetitive nature of the inoculation The results of the hematological tests were normal
rather than to rhEPO itself, 27-29 as they appeared with the when compared to their values before the start of the
same intensity in the placebo group. The results of the study. Differences were found in the groups inoculated
®
®
hematological tests were normal when compared to their with GBpoietin , Eprex , or the placebo in both single- and
values before the start of the study. repeated-dose studies. The values stayed within the
normal range for the species used in the study. 27,34 WBC
Body weight increased steadily and significantly
(P < 0.05) during the single-dose toxicity study; we found levels decreased within the normal range across all study
groups, including the control, with results being largely
similar differences in body weight in all study groups at similar. The absence of WBC count changes beyond the
different evaluation time points (days 0, 3, and 7). The normal range serves as evidence of the non-toxicity of
results were insignificant (P > 0.05) for the repeated-dose the test item under analysis. The high RBC count, HGB
35
toxicity study as well. The increase of this parameter in level, and HCT, together with the slight increase in PLT,
all the study groups translates into a normal evolution of confirm the therapeutic effect of EPO. These high counts
body weight for both genders indicating good health for of hematological parameters also reveal the therapeutical
the animals, further substantiating the non-toxicity of similarity of GBpoietin compared with Eprex . These
®
®
the GBpoietin in both studies. The absence of negative results are attributed to the mobilization of hematopoietic
®
effects on body weight gain is favorable for evaluating the progenitor cells to the peripheral blood, which is the
substance under study, as a decrease in body weight is one of reported mechanism of action of the product under study.
36
the primary clinical symptoms of stress or illness in this rat On the other hand, MCV increased in all groups under
strain. 30,31 Therefore, the increase in body weight is indirect study with Treatment-1 showing higher value than all other
evidence of non-toxicity for the substance under analysis. groups in the toxicity study. The differences in MCV levels
No significant changes in body temperature were observed among the groups were insignificant (P < 0.05). MCH
among the treatment groups. This result remained similar levels increased in Treatment-2, Treatment-3, and Control
when the same data were analyzed independently by groups, while they decreased in Treatment-1, Treatment-4,
gender or evaluation time points, which indicated normal and Placebo groups, though the values were within the
health for the animals, further supporting the non-toxicity normal range (P = 0.46) in all study groups. In single-
of the GBpoietin . Abnormal changes in body temperature dose toxicity study, MCHC levels decreased in all animal
®
under test conditions have been shown to indicate induced groups, while they decreased in Treatment-2 and Control
toxicity. 32,33 Accordingly, the absence of significant changes groups and increased in Treatment-1 and Placebo groups
in body temperature outside the normal range suggests in the repeat-dose toxicity study. The absence of change
that severe toxicity was unlikely in the test animals during in MCV, MCH, and MCHC levels outside the normal
the experiment. range demonstrates the non-toxicity of the test item under
Volume 8 Issue 2 (2025) 64 doi: 10.36922/itps.5797