Page 81 - ITPS-8-3
P. 81
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences Activity of green-synthesized nanoparticles
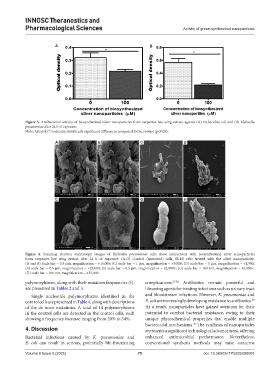
A B
Figure 3. Antibacterial activity of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles from carpenter bee wing extract against (A) Escherichia coli and (B) Klebsiella
pneumoniae after 24 h of exposure
Note: Asterisk (*) indicates statistically significant differences compared to the control (p<0.05).
A B C D
E F G H
Figure 4. Scanning electron microscopy images of Klebsiella pneumoniae cells show interactions with biosynthesized silver nanoparticles
from carpenter bee wing extract after 24 h of exposure. (A-D) Control (untreated) cells; (E-H) cells treated with the silver nanoparticles.
(A and B) Scale bar = 0.5 µm, magnification = ×15,000; (C) scale bar = 1 µm, magnification = ×9,000; (D) scale bar = 5 µm, magnification = ×1,900;
(E) scale bar = 0.5 µm, magnification = ×25,000; (F) scale bar = 0.5 µm, magnification = 22,000×; (G) scale bar = 100 nm, magnification = 45,000×;
(H) scale bar = 100 nm, magnification = ×35,000.
polymorphisms, along with their mutation frequencies (f), complications. 27,28 Antibiotics remain powerful and
are presented in Tables 2 and 3. lifesaving agents for treating infections such as urinary tract
Single nucleotide polymorphisms identified in the and bloodstream infections. However, K. pneumoniae and
29
control cells are presented in Table 4, along with descriptions E. coli are increasingly developing resistance to antibiotics.
of the de novo mutations. A total of 14 polymorphisms As a result, nanoparticles have gained attention for their
in the control cells are detected in the control cells, each potential to combat bacterial resistance, owing to their
showing a frequency increase ranging from 20% to 34%. unique physiochemical properties that enable multiple
30
bactericidal mechanisms. The synthesis of nanoparticles
4. Discussion represents a significant technological advancement, offering
Bacterial infections caused by K. pneumoniae and enhanced antimicrobial performance. Nevertheless,
E. coli can result in serious, potentially life-threatening conventional synthesis methods may raise concerns
Volume 8 Issue 3 (2025) 75 doi: 10.36922/ITPS025080007