Page 84 - ITPS-8-3
P. 84
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences Activity of green-synthesized nanoparticles
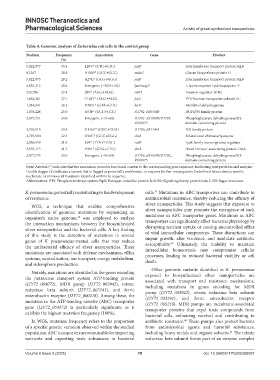
Table 4. Genomic analysis of Escherichia coli cells in the control group
Position Frequency Annotation Gene Product
(%)
5,022,977 35.4 L28V* (CTC→GTC) pqiB Intermembrane transport protein PqiB
82,367 29.6 A100P* (GCC→CCC) mdoG Glucan biosynthesis protein G
5,022,975 29.2 A27G* (GCG→GGG) pqiB Intermembrane transport protein PqiB
4,935,212 28.6 Intergenic (−362/+132) lysO/aqpZ L-lysine exporter LysO/aquaporin Z
325,706 27.4 S9R* (AGC→AGG) sirB2 Invasion regulator SirB2
1,664,261 27.1 T163T* (ACC→ACG) fryC PTS fructose transporter subunit IIC
1,244,541 26.2 V392L* (GTA→CTA) hisD Histidinol dehydrogenase
1,078,228 25.0 A53P* (GCC→CCC) D1792_RS05680 DUF4756 family protein
2,077,731 24.0 Intergenic (−7/+65) D1792_RS10070/D1792_ Phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase/SIS
RS10075 domain-containing protein
2,376,513 23.8 G116G* (GGC→GGA) D1792_RS11465 YtfJ family protein
2,725,980 22.5 G94G* (GGC→GGG) chiA Bifunctional chitinase/lysozyme
2,936,459 21.8 L94* (TTA→TGA) ‡ rcdB LysR family transcriptional regulator
2,555,115 21.5 V98L* (GTG→CTG) diaA DnaA initiator-associating protein DiaA
2,077,733 20.0 Intergenic (−9/+63) D1792_RS10070/D1792_ Phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase/SIS
RS10075 domain-containing protein
Note: Asterisk (*) indicates that the annotation provides functional context to the corresponding gene sequence, facilitating interpretation and analysis;
Double dagger (‡) indicates a variant that is flagged as potentially problematic or requires further investigation; Underlined letters denote specific
nucleotide or amino acid mutations identified within the sequence.
Abbreviations: PTS: Phosphotransferase system; PqiB: Paraquat-inducible protein B; SirB2: Signal regulatory protein beta 2; SIS: Sugar isomerase.
K. pneumoniae, potentially contributing to the development cells. Mutations in ABC transporters can contribute to
39
of resistance. antimicrobial resistance, thereby reducing the efficacy of
WGS, a technique that enables comprehensive silver nanoparticles. This study suggests that exposure to
identification of genomic mutations by sequencing an silver nanoparticles may promote the emergence of such
38
organism’s entire genome, was employed to analyze mutations in ABC transporter genes. Mutations in ABC
the interaction mechanisms between the biosynthesized transporters can significantly affect bacterial physiology by
silver nanoparticles and the bacterial cells. A key finding disrupting nutrient uptake or causing uncontrolled efflux
of this study is the detection of mutations in several of vital intracellular components. These disruptions can
genes of K. pneumoniae-treated cells that may reduce impair growth, alter virulence, and modulate antibiotic
susceptibility. Ultimately, the inability to maintain
39
the antibacterial efficacy of silver nanoparticles. These intracellular homeostasis may compromise cellular
mutations are associated with defense mechanisms, efflux
systems, neutralization, ion transport, energy metabolism, processes, leading to reduced bacterial viability or cell
death.
and siderophore production.
Other genomic variants identified in K. pneumoniae
Notably, mutations are identified in the genes encoding exposed to biosynthesized silver nanoparticles are
the putrescine transport system ATP-binding protein associated with transport and resistance mechanisms,
(J2Y72_004072), MDR pump (J2Y72_003942), nitrate including mutations in genes encoding for MDR
reductase beta subunit (J2Y72_003241), and ferric pump (J2Y72_003942), nitrate reductase beta subunit
enterobactin receptor (J2Y72_000218). Among these, the (J2Y72_003241), and ferric enterobactin receptor
mutation in the ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter (J2Y72_000218). MDR pumps are membrane-associated
gene (J2Y72_004072) is particularly significant, as it transporter proteins that expel toxic compounds from
exhibits the highest mutation frequency (100%). bacterial cells, enhancing survival and contributing to
In WGS, mutation frequency refers to the proportion antibiotic resistance. These pumps also protect bacteria
40
of a specific genetic variation observed within the studied from antimicrobial agents and harmful substances,
41
population. ABC transporters are responsible for importing including heavy metals and organic solvents. The nitrate
nutrients and exporting toxic substances in bacterial reductase beta subunit forms part of an enzyme complex
Volume 8 Issue 3 (2025) 78 doi: 10.36922/ITPS025080007