Page 82 - ITPS-8-3
P. 82
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences Activity of green-synthesized nanoparticles
A B C D
E F G H
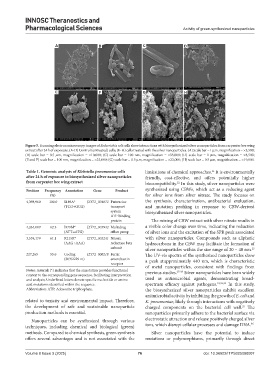
Figure 5. Scanning electron microscopy images of Escherichia coli cells show interactions with biosynthesized silver nanoparticles from carpenter bee wing
extract after 24 h of exposure. (A-D) Control (untreated) cells; (E-H) cells treated with the silver nanoparticles. (A) Scale bar = 1 µm, magnification = ×5,500;
(B) scale bar = 0.5 µm, magnification = ×10,000; (C) scale bar = 100 nm, magnification = ×33,000; (D) scale bar = 1 µm, magnification = ×8,500;
(E and F) scale bar = 100 nm, magnification = ×33,000; (G) scale bar = 0.5 µm, magnification = ×23,000; (H) scale bar = 0.5 µm, magnification = ×19,000.
Table 1. Genomic analysis of Klebsiella pneumoniae cells limitations of chemical approaches. It is environmentally
31
after 24 h of exposure to biosynthesized silver nanoparticles friendly, cost-effective, and offers potentially higher
from carpenter bee wing extract biocompatibility. In this study, silver nanoparticles were
32
Position Frequency Annotation Gene Product synthesized using CBWs, which act as a reducing agent
(%) for silver ions from silver nitrate. The study focuses on
4,398,960 100.0 S189A* J2Y72_004072 Putrescine the synthesis, characterization, antibacterial evaluation,
(TCG→GCG) transport and mutation profiling in response to CBW-derived
system biosynthesized silver nanoparticles.
ATP-binding
protein The mixing of CBW extract with silver nitrate results in
4,264,009 62.3 I879M* J2Y72_003942 Multidrug a visible color change over time, indicating the reduction
(ATT→ATG) efflux pump of silver ions and the excitation of the SPR peak associated
3,539,179 61.1 K215K* J2Y72_003241 Nitrate with silver nanoparticles. Compounds such as aliphatic
(AAG→AAA) reductase beta hydrocarbons in the CBW may facilitate the formation of
subunit silver nanoparticles within the size range of 20 – 40 nm.
25
227,265 55.6 Coding J2Y72_000218 Ferric The UV-vis spectra of the synthesized nanoparticles show
(303/2229 nt) enterobactin a peak at approximately 440 nm, which is characteristic
receptor of metal nanoparticles, consistent with findings from
Notes: Asterisk (*) indicates that the annotation provides functional previous studies. 25-33 Silver nanoparticles have been widely
context to the corresponding gene sequence, facilitating interpretation
and analysis; Underlined letters denote specific nucleotide or amino used as antimicrobial agents, demonstrating broad-
acid mutations identified within the sequence. spectrum efficacy against pathogens. 24,25,34 In this study,
Abbreviation: ATP: Adenosine triphosphate. the biosynthesized silver nanoparticles exhibit excellent
antimicrobial activity by inhibiting the growth of E. coli and
related to toxicity and environmental impact. Therefore, K. pneumoniae, likely through interactions with negatively
the development of safe and sustainable nanoparticle charged components on the bacterial cell wall. The
35
production methods is essential. nanoparticles primarily adhere to the bacterial surface via
Nanoparticles can be synthesized through various electrostatic attraction and release positively charged silver
techniques, including chemical and biological (green) ions, which disrupt cellular processes and damage DNA. 36
methods. Compared to chemical synthesis, green synthesis Silver nanoparticles have the potential to induce
offers several advantages and is not associated with the mutations or polymorphisms, primarily through direct
Volume 8 Issue 3 (2025) 76 doi: 10.36922/ITPS025080007