Page 94 - JCAU-6-2
P. 94
Journal of Chinese
Architecture and Urbanism Residential urban heritage space study
historic district, the accessibility of small alleys is relatively (c) Spatial topological structure comparative analysis
low, thus reducing their likelihood of being targeted by Based on the above analysis, both areas demonstrate a
“destination traffic.” trend of gradually decreasing centrality concerning Life
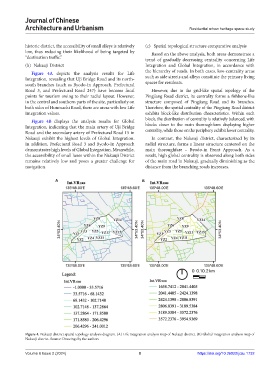
(b) Nakauji District Integration and Global Integration, in accordance with
Figure 4A depicts the analysis results for Life the hierarchy of roads. In both cases, low-centrality areas
Integration, revealing that Uji Bridge Road and its north- such as side streets and alleys constitute the primary living
south branches (such as Byodo-in Approach, Prefectural spaces for residents.
Road 3, and Prefectural Road 247) have become focal However, due to the grid-like spatial topology of the
points for tourism owing to their radial layout. However, Pingjiang Road district, its centrality forms a fishbone-like
in the central and southern parts of the site, particularly on structure composed of Pingjiang Road and its branches.
both sides of Honmachi Road, there are areas with low Life Therefore, the spatial centrality of the Pingjiang Road district
Integration values. exhibits block-like distribution characteristics. Within each
Figure 4B displays the analysis results for Global block, the distribution of centrality is relatively balanced, with
Integration, indicating that the main artery of Uji Bridge blocks closer to the main thoroughfares displaying higher
Road and the secondary artery of Prefectural Road 15 in centrality, while those on the periphery exhibit lower centrality.
Nakauji exhibit the highest levels of Global Integration. In contrast, the Nakauji district, characterized by its
In addition, Prefectural Road 3 and Byodo-in Approach radial structure, forms a linear structure centered on the
demonstrates high levels of Global Integration. Meanwhile, main thoroughfare – Byodo-in Front Approach. As a
the accessibility of small lanes within the Nakauji District result, high global centrality is observed along both sides
remains relatively low and poses a greater challenge for of the main road in Nakauji, gradually diminishing as the
navigation. distance from the branching roads increases.
A B
Figure 4. Nakauji district spatial topology analysis diagram. (A) Life integration analysis map of Nakauji district. (B) Global integration analysis map of
Nakauji district. Source: Drawings by the authors
Volume 6 Issue 2 (2024) 8 https://doi.org/10.36922/jcau.1732