Page 83 - JCAU-7-2
P. 83
Journal of Chinese
Architecture and Urbanism Spatial network analysis of hutongs
Table 2. Matrix representation of the spatial network
Node no. 0 1 2 3
0 0 1 1 9999
1 1 0 9999 1
2 1 9999 0 1
3 9999 1 1 0
Table 3. Depth values between nodes
Node no. Depth value
0 – 1 1
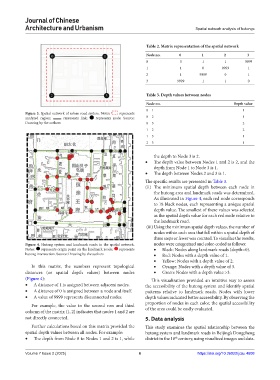
Figure 3. Spatial network of urban road system. Notes: represents
analyzed region; represents link; represents node. Source: 0 – 2 1
Drawing by the authors 0 – 3 2
1 – 2 2
1 – 3 1
2 – 3 1
the depth to Node 3 is 2.
• The depth value between Nodes 1 and 2 is 2, and the
depth from Node 1 to Node 3 is 1.
• The depth between Nodes 2 and 3 is 1.
The specific results are presented in Table 3.
(ii) The minimum spatial depth between each node in
the hutong area and landmark roads was determined.
As illustrated in Figure 4, each red node corresponds
to 18 black nodes, each representing a unique spatial
depth value. The smallest of these values was selected
as the spatial depth value for each red node relative to
the landmark road.
(iii) Using the minimum spatial depth values, the number of
nodes within each area that fall within a spatial depth of
three steps or fewer was counted. To visualize the results,
Figure 4. Hutong system and landmark roads in the spatial network. nodes were categorized and color-coded as follows:
Notes: represents origin point on the landmark roads; represents • Black: Nodes along landmark roads (depth=0).
hutong intersection. Source: Drawing by the authors • Red: Nodes with a depth value of 1.
• Yellow: Nodes with a depth value of 2.
In this matrix, the numbers represent topological • Orange: Nodes with a depth value of 3.
distances (or spatial depth values) between nodes • Green: Nodes with a depth value >3.
(Figure 4): This visualization provided an intuitive way to assess
• A distance of 1 is assigned between adjacent nodes. the accessibility of the hutong system and identify spatial
• A distance of 0 is assigned between a node and itself. patterns relative to landmark roads. Nodes with lower
• A value of 9999 represents disconnected nodes. depth values indicated better accessibility. By observing the
proportion of nodes in each color, the spatial accessibility
For example, the value in the second row and third of the area could be easily evaluated.
column of the matrix (1, 2) indicates that nodes 1 and 2 are
not directly connected. 5. Data analysis
Further calculations based on this matrix provided the This study examines the spatial relationship between the
spatial depth values between all nodes. For example: hutong system and landmark roads in Beijing’s Dongcheng
• The depth from Node 0 to Nodes 1 and 2 is 1, while district in the 18 century, using visualized images and data.
th
Volume 7 Issue 2 (2025) 6 https://doi.org/10.36922/jcau.4608