Page 24 - JCBP-2-4
P. 24
Journal of Clinical and
Basic Psychosomatics Genetic factors and personality disorders
of engaging in heroin use, which could potentially result in characteristics of individuals with heroin dependence. In
alterations to their personality. The clinical manifestation comparison to control subjects, the individuals with heroin
of addiction primarily revolves around mood and impulse- dependence exhibited elevated scores for personality traits
control dysregulation while heroin dependence has a related to novelty seeking and harm avoidance. In addition,
12
negative effect on impulse control. People with specific a variation in the gene responsible for producing catechol-
13
personality characteristics, such as a tendency for risk- O-methyltransferase (COMT) has been demonstrated to
taking behaviors, may demonstrate a predisposition impact human executive cognition and the functioning of
14
towards heroin use. For instance, a prior study indicated the prefrontal cortex and this influence is likely due to its
that antisocial personality disorder was the only domain effect on prefrontal dopamine signaling. Moreover, the
22
23
where a cumulative risk was observed for heroin overdose. COMT gene can play a role in personality traits. Certain
Antisocial personality disorder is frequently identified as variations (polymorphisms) of the COMT gene can result
the predominant comorbid diagnosis among individuals in different levels of enzyme activity, leading to variations
with substance abuse issues. 15,16 Furthermore, it is crucial in dopamine regulation.
to emphasize that an individual’s personality traits may Collectively, our goal was to investigate single nucleotide
influence their preference for a particular drug. A previous polymorphisms (SNPs) of COMT and those related
study has identified a specific externalizing dimension to stress, as well as their relationship with personality
17
that distinguishes heroin users from those who use alcohol, disorders among women with heroin dependence.
marijuana, and cocaine. This suggests that certain personality
traits may be associated with a higher likelihood of choosing 2. Methods
heroin over other substances. Nevertheless, it remains The study protocol was authorized by the review boards
uncertain which specific personality traits have an impact at the Shanghai Mental Health Center (SHMC), School
on the preference for heroin over other substances. of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University. The research
Furthermore, the use of heroin may be linked to several adhered to the principles outlined in the Declaration of
personality disorders, such as schizoid, depressive, and Helsinki. All patients gave their informed consent, prior
paranoid personalities. Schizoid and depressive personality to participating in the study. Furthermore, meticulous
disorders have been found to be associated with feelings records were kept to document the number of interviews
of loneliness, and individuals experiencing loneliness may conducted with each patient for precise record-keeping.
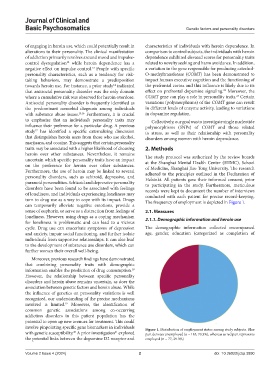
turn to drug use as a way to cope with its impact. Drugs The frequency of employment is depicted in Figure 1.
can temporarily alleviate negative emotions, provide a
sense of euphoria, or serve as a distraction from feelings of 2.1. Measures
loneliness. However, using drugs as a coping mechanism 2.1.1. Demographic information and heroin use
for loneliness is problematic and can lead to a vicious
cycle. Drug use can exacerbate symptoms of depression The demographic information collected encompassed
and anxiety, impair social functioning, and further isolate age, gender, education (categorized as completion of
individuals from supportive relationships. It can also lead
to the development of substance use disorders, which can
further worsen their overall well-being.
Moreover, previous research findings have demonstrated
that combining personality traits with demographic
information enables the prediction of drug consumption.
18
However, the relationship between specific personality
disorders and heroin abuse remains uncertain, as does the
association between genetic factors and heroin abuse. While
the influence of genetics on personality variations is well
recognized, our understanding of the precise mechanisms
involved is limited. Moreover, the identification of
19
common genetic associations among co-occurring
addiction disorders in this patient population has the
potential to open up new avenues for treatment. This could
involve pinpointing specific gene biomarkers in individuals Figure 1. Distribution of employment status among study subjects. Blue
with genetic susceptibility. A prior investigation explored part denotes unemployed (n = 185, 70.3%), whereas as red part represents
21
20
the potential links between the dopamine D2 receptor and employed (n = 77, 29.3%)
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2024) 2 doi: 10.36922/jcbp.3890