Page 37 - JCTR-10-2
P. 37
Abtahi et al. | Journal of Clinical and Translational Research 2024; 10(2): 119-140 131
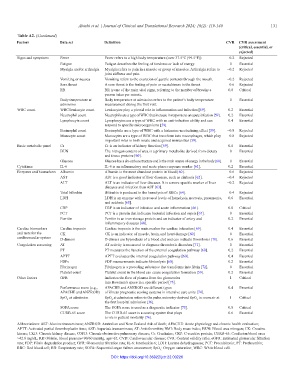
Table A2. (Continued)
Factors Data set Definition CVR CVR assessment
(critical, essential, or
rejected)
Signs and symptoms Fever Fever refers to a high body temperature (over 37.5°C [99.5°F]). −0.2 Rejected
Fatigue Fatigue describes the feeling of tiredness or lack of energy. 0 Essential
Myalgia and/or arthralgia Myalgia refers to pain in a muscle or group of muscles. Arthralgia refers to −0.2 Rejected
joint stiffness and pain.
Vomiting or nausea Vomiting refers to the excretion of gastric contents through the mouth. −0.2 Rejected
Sore throat A sore throat is the feeling of pain or scratchiness in the throat. −0.6 Rejected
RR RR is one of the main vital signs, referring to the number of breaths a 0.8 Critical
person takes per minute.
Body temperature at Body temperature at admission refers to the patient’s body temperature 0 Essential
admission measurement during the first visit.
WBC count WBC/leukocyte count Leukocytes play a pivotal role in inflammation and infection [59]. 0.2 Essential
Neutrophil count Neutrophils are a type of WBC that increase in response to an acute infection [59]. 0.2 Essential
Lymphocyte count Lymphocytes are a type of WBC with an anti-infection ability and can 0.4 Essential
respond to specific microorganisms [59].
Eosinophil count Eosinophils are a type of WBC with a histamine-neutralizing effect [59]. −0.8 Rejected
Monocyte count Monocytes are a type of WBC that transform into macrophages, which play −0.8 Rejected
important roles in both innate and acquired immunities [59].
Basic metabolic panel Cr Cr is an indicator of kidney function [59]. 0.6 Essential
BUN The nitrogen content of urea is a primary metabolite derived from dietary 0 Essential
and tissue proteins [60].
Glucose Glucose has a six-carbon structure and is the main source of energy in the body [60]. 0 Essential
Cytokines IL-6 IL-6 is an inflammatory and acute phase response marker [61]. 0.2 Essential
Enzymes and biomarkers Albumin Albumin is the most abundant protein in blood [60]. −0.6 Rejected
AST AST is a good indicator of liver diseases, such as cirrhosis [62]. −0.4 Rejected
ALT ALT is an indicator of liver diseases. It is a more specific marker of liver −0.2 Rejected
diseases and infection than AST [63].
Total bilirubin Bilirubin is produced in the hemolysis of RBCs [64]. −0.4 Rejected
LDH LDH is an enzyme with increased levels of hemolysis, necrosis, pneumonia, 0.6 Essential
and acidosis [65].
CRP CRP is an indicator of infection and acute inflammation [66]. 0.8 Critical
PCT PCT is a protein that indicates bacterial infection and sepsis [67]. 0 Essential
Ferritin Ferritin is an iron-storage protein and an indicator of artery and 0.2 Essential
inflammatory diseases [68].
Cardiac biomarkers Cardiac troponin Cardiac troponin is the main marker for cardiac infarction [69]. 0.4 Essential
and tests for the CK CK is an indicator of muscle, brain, and heart damage [60] 0 Essential
cardiovascular system D-dimers D-dimers are byproducts of a blood clot and can indicate thrombosis [70]. 0.6 Essential
Coagulation screening AT AT activity is measured to diagnose thrombotic disorders [71]. 0 Essential
PT PT measures the function of the external coagulation pathway [60]. 0.2 Essential
APTT APTT evaluates the internal coagulation pathway [60]. 0.4 Essential
FDPs FDP measurements indicate fibrinolysis [60]. 0.2 Essential
Fibrinogen Fibrinogen is a preceding substance that transforms into fibrin [72]. 0 Essential
Platelet count Platelet count in the blood can cause coagulation formation [59]. 0.2 Essential
Other factors GFR Indicates the flow of plasma from the glomerulus 1 Critical
into Bowman’s space in a specific period [73].
Performance score (e.g., APACHE and ANZROD are different types 0.4 Essential
APACHE and ANZROD) of illness prognostic scoring systems in intensive care units [74].
SpO at admission SpO at admission refers to the pulse oximetry-derived SpO in room air at 1 Critical
2
2
2
the first hospital admission [36].
SOFA score The SOFA score is used as a diagnostic indicator [75]. 0.8 Critical
CURB-65 score The CURB-65 score is a scoring system that plays 0.6 Essential
a role in patient mortality [76].
Abbreviations: ALT: Alanine transaminase; ANZROD: Australian and New Zealand risk of death; APACHE: Acute physiology and chronic health evaluation;
APTT: Activated partial thromboplastin time; AST: Aspartate transaminase; AT: Anti-thrombin; BMI: Body mass index; BUN: Blood urea nitrogen; CK: Creatine
kinase; CKD: Chronic kidney disease; COPD: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; Cr: Creatinine; CRP: C-reactive protein; CURB-65: Confusion blood urea
>42.8 mg/dL, RR>30/min, blood pressure<90/60 mmHg, age>65; CVD: Cardiovascular disease; CVR: Content validity ratio; eGFR: Estimated glomerular filtration
rate; FDP: Fibrin degradation product; GFR: Glomerular filtration rate; IL-6: Interleukin-6; LDH: Lactate dehydrogenase; PCT: Procalcitonin; PT: Prothrombin;
RBC: Red blood cell; RR: Respiratory rate; SOFA: Sequential organ failure assessment; SpO : Oxygen saturation; WBC: White blood cell.
2
DOI: https://doi.org/10.36922/jctr.22.00226