Page 38 - JCTR-10-2
P. 38
132 Abtahi et al. | Journal of Clinical and Translational Research 2024; 10(2): 119-140
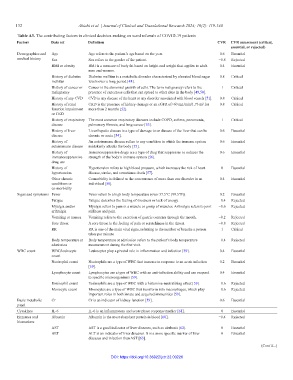
Table A3. The contributing factors in clinical decision-making on ward referrals of COVID-19 patients
Factors Data set Definition CVR CVR assessment (critical,
essential, or rejected)
Demographics and Age Age refers to the patient’s age based on the year. 0.6 Essential
medical history Sex Sex refers to the gender of the patient. −0.8 Rejected
BMI or obesity BMI is a measure of body fat based on height and weight that applies to adult 0.4 Essential
men and women.
History of diabetes Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disorder characterized by elevated blood sugar 0.8 Critical
mellitus levels over a long period [48].
History of cancer or Cancer is the abnormal growth of cells. The term malignancy refers to the 1 Critical
malignancy presence of cancerous cells that can spread to other sites in the body [49,50].
History of any CVD CVD is any disease of the heart or any disorder associated with blood vessels [51]. 0.8 Critical
History of renal CKD is the presence of kidney damage or an eGFR of<60 mL/min/1.73 m for 0.8 Critical
2
function impairment more than 2 months [52].
or CKD
History of respiratory The most common respiratory diseases include COPD, asthma, pneumonia, 1 Critical
disease pulmonary fibrosis, and lung cancer [53].
History of liver Liver/hepatic disease is a type of damage to or disease of the liver that can be 0.6 Essential
disease chronic or acute [54].
History of An autoimmune disease refers to any condition in which the immune system 0.6 Essential
autoimmune disease mistakenly attacks the body [55].
History of Immunosuppressive drugs are a type of drug that suppresses or reduces the 0.6 Essential
immunosuppressive strength of the body’s immune system [56].
drug use
History of Hypertension refers to high blood pressure, which increases the risk of heart 0 Essential
hypertension disease, stroke, and sometimes death [57].
Other chronic Comorbidity is defined as the concurrence of more than one disorder in an 0.4 Essential
conditions or individual [58].
co-morbidity
Signs and symptoms Fever Fever refers to a high body temperature (over 37.5°C [99.5°F]). 0.2 Essential
Fatigue Fatigue describes the feeling of tiredness or lack of energy. −0.4 Rejected
Myalgia and/or Myalgia refers to pain in a muscle or group of muscles. Arthralgia refers to joint −0.6 Rejected
arthralgia stiffness and pain.
Vomiting or nausea Vomiting refers to the excretion of gastric contents through the mouth. −0.2 Rejected
Sore throat A sore throat is the feeling of pain or scratchiness in the throat. −0.8 Rejected
RR RR is one of the main vital signs, referring to the number of breaths a person 1 Critical
takes per minute
Body temperature at Body temperature at admission refers to the patient’s body temperature −0.4 Rejected
admission measurement during the first visit.
WBC count WBC/leukocyte Leukocytes play a pivotal role in inflammation and infection [59]. 0.4 Essential
count
Neutrophil count Neutrophils are a type of WBC that increase in response to an acute infection 0.2 Essential
[59].
Lymphocyte count Lymphocytes are a type of WBC with an anti-infection ability and can respond 0.4 Essential
to specific microorganisms [59].
Eosinophil count Eosinophils are a type of WBC with a histamine-neutralizing effect [59]. −0.6 Rejected
Monocyte count Monocytes are a type of WBC that transform into macrophages, which play −0.6 Rejected
important roles in both innate and acquired immunities [59].
Basic metabolic Cr Cr is an indicator of kidney function [59]. 0.6 Essential
panel
Cytokines IL-6 IL-6 is an inflammatory and acute phase response marker [61]. 0 Essential
Enzymes and Albumin Albumin is the most abundant protein in blood [60]. −0.4 Rejected
biomarkers
AST AST is a good indicator of liver diseases, such as cirrhosis [62]. 0 Essential
ALT ALT is an indicator of liver diseases. It is a more specific marker of liver 0 Essential
diseases and infection than AST [63].
(Cont’d...)
DOI: https://doi.org/10.36922/jctr.22.00226