Page 52 - JCTR-10-2
P. 52
146 Grondin et al. | Journal of Clinical and Translational Research 2024; 10(2): 141-150
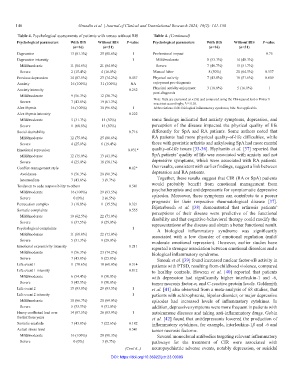
Table 4. Psychological assessments of patients with versus without BIS Table 4. (Continued)
Psychological parameters With BIS Without BIS P‑value Psychological parameters With BIS Without BIS P‑value
(n=16) (n=31) (n=16) (n=31)
Depression 13 (81.3%) 25 (80.6%) 1 Professional impact 0.75
Depression intensity 1 Mild/moderate 8 (53.3%) 14 (48.3%)
Mild/moderate 11 (84.6%) 21 (84.0%) Severe 7 (46.7%) 15 (51.7%)
Severe 2 (15.4%) 4 (16.0%) Manual labor 8 (50%) 20 (64.5%) 0.337
Previous depression 14 (87.5%) 23 (74.2%) 0.457 Physical activity 7 (43.8%) 16 (51.6%) 0.609
Anxiety 16 (100%) 31 (100%) NA enjoyment pre-diagnosis
Anxiety intensity 0.252 Physical activity enjoyment 3 (18.8%) 5 (16.1%) 1
Mild/moderate 9 (56.3%) 12 (38.7%) post-diagnosis
Severe 7 (43.8%) 19 (61.3%) Note: Data are expressed as n (%) and compared using the Chi-squared test or Fisher’s
exact test accordingly; *P<0.05.
Alexithymia 16 (100%) 30 (96.8%) 1 Abbreviations: BIS: Biological inflammatory syndrome; NA: Not applicable.
Alexithymia intensity 0.222
Mild/moderate 5 (31.3%) 15 (50%) some findings indicated that anxiety symptoms, depression, and
Severe 11 (68.8%) 15 (50%) perception of the disease impacted the physical quality of life
Social desirability 0.716 differently for SpA and RA patients. Some authors noted that
Mild/moderate 12 (75.0%) 25 (80.6%) RA patients had more physical quality-of-life difficulties, while
Severe 4 (25.0%) 6 (19.4%) those with psoriatic arthritis and ankylosing SpA had more mental
Emotional repression 0.031* quality-of-life issues [33-36]. Hyphantis et al. [37] reported that
Mild/moderate 12 (75.0%) 13 (41.9%) SpA patients’ quality of life was associated with anxiety and not
Severe 4 (25.0%) 18 (58.1%) depressive symptoms, which were associated with RA patients.
Conflict-management style 0.02* Our results, consistent with earlier findings, suggest a link between
Avoidance 9 (56.3%) 28 (90.3%) depression and RA patients.
Intermediate 7 (43.8%) 3 (9.7%) Together, these results suggest that CIR (RA or SpA) patients
Tendency to cede responsibility to others 0.541 would probably benefit from emotional management from
Mild/moderate 16 (100%) 29 (93.5%) psychotherapists and antidepressants for symptomatic depressive
Severe 0 (0%) 2 (6.5%) episodes. Moreover, these symptoms can contribute to a poorer
Persecution complex 3 (18.8%) 11 (35.5%) 0.321 prognosis for their respective rheumatological disease [37].
Bijsterbosch et al. [38] demonstrated that arthrosis patients’
Somatic complaints 0.555
Mild/moderate 10 (62.5%) 22 (71.0%) perceptions of their disease were predictive of the functional
disability and that cognitive-behavioral therapy could modify the
Severe 6 (37.5%) 9 (29.0%) representations of the disease and obtain a better functional result.
Psychological complaints 1 A biological inflammatory syndrome was significantly
Mild/moderate 11 (68.8%) 22 (71.0%) associated with a low disorder of emotional regulation (mild/
Severe 5 (31.3%) 9 (29.0%) moderate emotional repression). However, earlier studies have
Emotional expressivity intensity 0.211 reported a stronger association between emotional disorders and a
Mild/moderate 9 (56.3%) 23 (74.2%) biological inflammatory syndrome.
Severe 7 (43.8%) 8 (25.8%) Smoak et al. [39] found increased nuclear factor-κB activity in
Life event 1 11 (78.6%) 18 (60.0%) 0.314 patients with PTSD, resulting from childhood violence, compared
Life event 1 intensity 0.812 to healthy controls. Howren et al. [40] reported that patients
Mild/moderate 6 (54.4%) 9 (50.0%) with depression had significantly higher interleukin-1 and -6,
Severe 5 (45.5%) 9 (50.0%) tumor necrosis factor-α, and C-reactive protein levels. Goldsmith
Life event 2 15 (93.8%) 29 (93.5%) 1 et al. [41] also observed from a meta-analysis of 68 studies, that
Life event 2 intensity 1 patients with schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, or major depressive
Mild/moderate 10 (66.7%) 20 (69.0%) episodes had increased levels of inflammatory cytokines. In
Severe 5 (33.3%) 9 (31.0%) addition, depressive symptoms were more frequent in patients with
Heavy conflictual load over 14 (87.5%) 26 (83.9%) 1 autoimmune diseases and taking anti-inflammatory drugs. Gobin
the last three years et al. [42] found that antidepressants lowered the production of
Somatic escalade 7 (43.8%) 7 (22.6%) 0.182 inflammatory cytokines, for example, interleukins-1β and -6 and
Actual stress level 0.541 tumor necrosis factor-α.
Mild/moderate 16 (100%) 28 (90.3%) Several monoclonal antibodies targeting relevant inflammatory
Severe 0 (0%) 3 (9.7%) pathways for the treatment of CIR were associated with
(Cont’d...) neuropsychiatric adverse events, notably depression, or suicidal
DOI: https://doi.org/10.36922/jctr.23.00099