Page 12 - JCTR-10-3
P. 12
186 Xie et al. | Journal of Clinical and Translational Research 2024; 10(3): 180-190
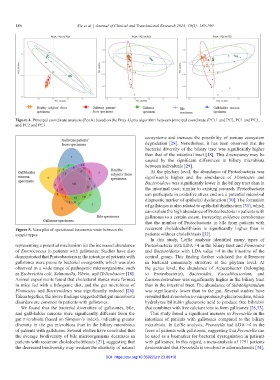
Figure 4. Principal coordinate analysis (PcoA) based on the Bray-Curtis algorithm between principal coordinate (PC) 1 and PC2, PC1 and PC3,
and PC2 and PC3.
ecosystems and increase the possibility of serious ecosystem
degradation [28]. Nonetheless, it has been observed that the
bacterial diversity of the biliary tract was significantly higher
than that of the intestinal tract [18]. This discrepancy may be
caused by the significant differences in biliary microbiota
between individuals [29].
At the phylum level, the abundance of Proteobacteria was
significantly higher and the abundance of Firmicutes and
Bacteroidetes was significantly lower in the biliary tract than in
the intestinal tract, similar to existing research. Proteobacteria
can participate in oxidative stress and are a potential microbial
diagnostic marker of epithelial dysfunction [30]. The formation
of gallstones is also related to epithelial dysfunction [31], which
can explain the high abundance of Proteobacteria in patients with
gallstones to a certain extent. Increasing evidence corroborates
that the number of Proteobacteria in bile from patients with
Figure 5. Venn plot of operational taxonomic units between the recurrent choledocholithiasis is significantly higher than in
sample types. patients without cholelithiasis [32].
In this study, LefSe analysis identified many types of
representing a potential mechanism for the increased abundance Proteobacteria with LDA >4 in the biliary tract and Firmicutes
of Enterococcus in patients with gallstones. Studies have also and Bacteroidetes with LDA value >4 in the intestine of the
demonstrated that Proteobacteria in the intestine of patients with control group. This finding further validated the differences
gallstones were prone to bacterial overgrowth, which was also in bacterial community structure at the phylum level. At
observed in a wide range of pathogenic microorganisms, such the genus level, the abundance of Acinetobacter (belonging
as Escherichia coli, Salmonella, Vibrio, and Helicobacter [18]. to Proteobacteria), Bacteroides, Faecalibacterium, and
Animal experiments found that cholesterol stones were formed Lachnoclostridium was significantly higher in the biliary tract
in mice fed with a lithogenic diet, and the gut microbiota of than in the intestinal tract. The abundance of Subdoligranulum
Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes was significantly reduced [26]. was significantly lower than in the gut. Several studies have
Taken together, the above findings suggested that gut microbiota revealed that Acinetobacter can produce β-glucuronidase, which
disorders are common in patients with gallstones. hydrolyzes bilirubin glucuronic acid to produce free bilirubin
We found that the bacterial diversities of gallstones, bile, that combines with free calcium ions to form gallstones [25,33].
and gallbladder mucosa were significantly different from the This study found a significant increase in Prevotella in the
gut microbiota (based on Simpson’s index), indicating greater intestines of patients with gallstones compared to the biliary
diversity in the gut microbiota than in the biliary microbiota microbiota. In LefSe analysis, Prevotella had LDA >4 in the
of patients with gallstones. Several studies have concluded that feces of patients with gallstones, suggesting that Prevotella can
the average biodiversity of bile microorganisms decreases in be used as a biomarker for bacterial dysregulation in patients
patients with recurrent choledocholithiasis [27], suggesting that with gallstones. In this regard, a meta-analysis of 1791 patients
the decreased biodiversity may weaken the elasticity of natural demonstrated that Prevotella is involved in atherosclerosis [34],
DOI: https://doi.org/10.36922/jctr.23.00118