Page 12 - JCTR-10-5
P. 12
274 Schirato et al. | Journal of Clinical and Translational Research 2024; 10(5): 269-282
Figure 1. Mean SDNN (left) and RMSSD (right) of pre- and post-dive data for each decompression profile (n = 23)
Abbreviations: SDNN: Standard deviation of the normal-to-normal R-R interval; RMSSD: Square root of the mean squared differences of successive
R-R intervals
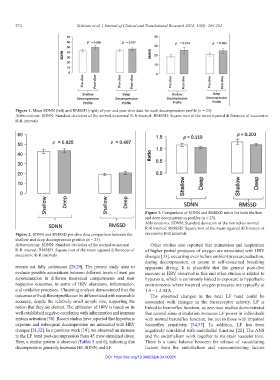
Figure 3. Comparison of SDNN and RMSSD ratios for both shallow
and deep decompression profiles (n = 23)
Abbreviations: SDNN: Standard deviation of the normal-to-normal
R-R interval; RMSSD: Square root of the mean squared differences of
Figure 2. SDNN and RMSSD pre-dive data comparison between the successive R-R intervals
shallow and deep decompression profiles (n = 23)
Abbreviations: SDNN: Standard deviation of the normal-to-normal Other studies also reported that immersion and inspiration
R-R interval; RMSSD: Square root of the mean squared differences of of higher partial pressures of oxygen are associated with HRV
successive R-R intervals changes [33], occurring even before ambient pressure reduction,
during decompression, or ascent in self-contained breathing
remain not fully understood [28,29]. The present study aims to apparatus diving. It is plausible that the general post-dive
evaluate possible associations between different levels of inert gas increase in HRV observed in this and other studies is related to
supersaturation in different theoretical compartments and their hyperoxia, which is commonly linked to exposure to hyperbaric
respective outcomes, in terms of HRV alterations, inflammation, environments where inspired oxygen pressures are typically at
and oxidative processes. Clustering analysis demonstrated that the 1.0 – 1.2 ATA.
outcomes of the different profiles can be differentiated with reasonable The observed changes in the total LF band could be
accuracy, despite the relatively small sample size, supporting the associated with changes in the baroreceptor activity. LF is
notion that they are distinct. The utilization of HRV is based on its linked to baroreflex function, as previous studies demonstrated
well-established negative correlation with inflammation and immune that carotid sinus stimulation increases LF power in individuals
system activation [30]. Recent studies have reported that hyperbaric with normal baroreflex function, but not in those with impaired
exposure and subsequent decompression are associated with HRV baroreflex sensitivity [34,35]. In addition, LF has been
changes [31,32]. In a previous work [18], we observed an increase negatively correlated with endothelial function [22]. The ANS
in the LF band post-decompression from 45 msw-simulated dives. and the endothelium work together to maintain vascular tone.
Here, a similar pattern is observed (Tables 5 and 6), indicating that There is a tonic balance between the release of vasodilating
decompression generally increases HF, SDNN, and LF. factors from the endothelium and vasoconstricting factors
DOI: https://doi.org/10.36922/jctr.24.00021