Page 14 - JCTR-10-5
P. 14
276 Schirato et al. | Journal of Clinical and Translational Research 2024; 10(5): 269-282
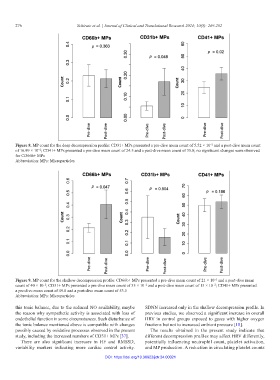
Figure 8. MP count for the deep decompression profile: CD31+ MPs presented a pre-dive mean count of 5.52 × 10 and a post-dive mean count
−2
of 16.99 × 10 ; CD41+ MPs presented a pre-dive mean count of 24.5 and a post-dive mean count of 35.8; no significant changes were observed
−2
for CD66b+ MPs
Abbreviation: MPs: Microparticles
Figure 9. MP count for the shallow decompression profile: CD66b+ MPs presented a pre-dive mean count of 21 × 10 and a post-dive mean
−2
count of 40 × 10 ; CD31+ MPs presented a pre-dive mean count of 35 × 10 and a post-dive mean count of 15 × 10 ; CD41+ MPs presented
−2
−2
−2
a pre-dive mean count of 49.8 and a post-dive mean count of 53.5
Abbreviation: MPs: Microparticles
this tonic balance, due to the reduced NO availability, maybe SDNN increased only in the shallow decompression profile. In
the reason why sympathetic activity is associated with loss of previous studies, we observed a significant increase in overall
endothelial function in some circumstances. Such disturbance of HRV in control groups exposed to gases with higher oxygen
the tonic balance mentioned above is compatible with changes fractions but not to increased ambient pressure [18].
possibly caused by oxidative processes observed in the present The results obtained in the present study indicate that
study, including the increased numbers of CD31+ MPs [37]. different decompression profiles may affect HRV differently,
There are also significant increases in HF and RMSSD, potentially influencing neutrophil count, platelet activation,
variability markers indicating more cardiac control activity. and MP production. A reduction in circulating platelet counts
DOI: https://doi.org/10.36922/jctr.24.00021