Page 68 - JCTR-11-1
P. 68
Journal of Clinical and
Translational Research Osteoporosis risk factors in diabetics
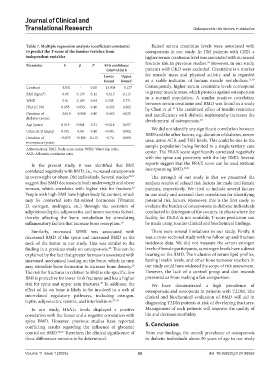
Table 7. Multiple regression analysis (coefficient constants) Raised serum creatinine levels were associated with
to predict the T-score of the lumbar vertebra from osteoporosis in our study. In DM patients with CKD, a
independent variables higher serum creatinine level was associated with increased
fracture risk in previous studies. However, in our study,
36
Parameter b β P 95% confidence
interval for b patients with CKD were excluded. Creatinine is a marker
Lower Upper for muscle mass and physical activity and is regarded
bound bound as a stable indicator of human muscle metabolism. 37,38
Constant −9.531 - 0.00 −13.934 −5.127 Consequently, higher serum creatinine levels correspond
BMI (kg/m ) 0.05 0.139 0.12 −0.013 0.113 to greater muscle mass, which protects against osteoporosis
2
WHR 5.01 0.185 0.04 0.248 9.771 in a normal population. A similar positive correlation
between serum creatinine and BMD was found in a study
HbA1C (%) 0.055 0.053 0.46 −0.092 0.202 by Chen et al. The combined effect of insulin resistance
39
Duration of −0.019 −0.068 0.40 −0.063 0.025 and insufficiency with diabetic nephropathy increases the
diabetes (years) development of osteoporosis. 10
Age (years) 0.019 0.081 0.31 −0.018 0.057
We did not identify any significant correlation between
Urine ACR (mg/g) 0.001 0.06 0.40 −0.001 0.002 BMD and the other factors, e.g., duration of diabetes, serum
Duration of −0.033 −0.186 0.113 −0.74 0.008 urea, urine ACR, and TSH levels. This could be due to the
menopause (years)
Abbreviations: BMI: Body mass index; WHR: Waist-hip ratio; sample population being limited to a single tertiary care
ACR: Albumin-creatinine ratio. center. The FRAX score significantly correlated negatively
with the spine and positively with the hip BMD. Several
In the present study, it was identified that BMI reports suggest that the FRAX score can be used without
correlated negatively with BMD, i.e., increased osteoporosis incorporating BMD. 40,41
in overweight or obese DM individuals. Several studies 26,27 The strength of our study is that we presented the
suggest that BMD decreases in both underweight and obese analysis results of related risk factors for male and female
women, which correlates with higher risk for fracture. patients, respectively. We tried to include several factors
28
People with high BMI have higher body fat content, which in our study and assessed their correlation for identifying
may be converted into fat-related hormones (Vitamin potential risk factors. Moreover, this is the first study to
D, estrogen, androgen, etc.) through the secretion of evaluate the burden of osteoporosis in diabetic individuals
adipokines (leptin, adiponectin, and tumor necrosis factor), conducted in this region of the country. In places where the
thereby affecting the bone metabolism by stimulating facility for DEXA is not available, T-score prediction can
inflammatory factors that increase bone resorption. 26 be made using routine clinical and biochemical findings.
Similarly, increased WHR was associated with There were several limitations in our study. Firstly, it
decreased BMD of the spine and increased BMD in the was a cross-sectional study with no follow-up and fracture
neck of the femur in our study. This was similar to the incidence data. We did not measure the serum estrogen
finding in a previous study on osteoporosis. This can be levels of female participants, as estrogen levels have a direct
28
explained by the fact that greater fat mass is associated with bearing on the BMD. The inclusion of serum lipid profiles,
increased mechanical loading on the bone, which in turn fasting insulin levels, and other bone turnover markers in
may stimulate bone formation to increase bone density. our study could have widened the scope of risk assessment.
29
The risk for fractures in relation to BMI is site-specific; low However, the lack of a control group and diet records
BMI is protective for lower limb fractures and has a higher prevented us from making a fair comparison.
risk for spine and upper arm fractures. In addition, the We have demonstrated a high prevalence of
30
effect of fat on bone is likely to be involved in a web of osteoporosis and osteopenia in patients with T2DM. The
interrelated regulatory pathways, including estrogen, clinical and biochemical evaluation of BMD will aid in
leptin, adiponectin, resistin, and interleukin-6. 31-33 diagnosing T2DM patients at risk of developing fractures.
In our study, HbA1c levels displayed a positive Management of such patients will improve the quality of
correlation with the femur and a negative correlation with life and decrease morbidity.
spine BMD. However, previous studies have reported 5. Conclusion
conflicting results regarding the influence of glycemic
control on BMD. 34,35 Therefore, the clinical significance of From our findings, the overall prevalence of osteoporosis
these differences remains to be determined. in diabetic individuals above 50 years of age in our study
Volume 11 Issue 1 (2025) 62 doi: 10.36922/jctr.24.00062