Page 54 - JCTR-11-2
P. 54
Journal of Clinical and
Translational Research CMV secular trends and race
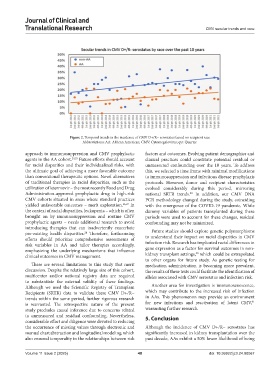
Figure 2. Temporal trends in the incidence of CMV D+/R− serostatus based on recipient race
Abbreviations: AA: African American; CMV: Cytomegalovirus; qtr: Quarter.
approach to immunosuppression and CMV prophylactic factors and outcomes. Evolving patient demographics and
agents in the AA cohort. 24,25 Future efforts should account clinical practices could constitute potential residual or
for racial disparities and their individualized risks, with unmeasured confounding over the 10 years. To address
the ultimate goal of achieving a more favorable outcome this, we selected a time frame with minimal modifications
than conventional therapeutic options. Novel alternatives to immunosuppression and infectious disease prophylaxis
of traditional therapies in racial disparities, such as the protocols. However, donor and recipient characteristics
utilization of letermovir – the most recently Food and Drug evolved considerably during this period, mirroring
Administration-approved prophylactic drug in high-risk national SRTR trends. In addition, our CMV DNA
29
CMV cohorts situated in areas where standard practices PCR methodology changed during the study, coinciding
yielded unfavorable outcomes – merit exploration. 26,27 In with the emergence of the COVID-19 pandemic. While
the context of racial disparities, leukopenia – which is often dummy variables of patients transplanted during these
brought on by immunosuppression and routine CMV periods were used to account for these changes, residual
prophylactic agents – needs additional research to avoid confounding may not be minimized.
introducing therapies that can inadvertently exacerbate
28
pre-existing health disparities. Therefore, forthcoming Future studies should explore genetic polymorphisms
efforts should prioritize comprehensive assessments of to understand their impact on racial disparities in CMV
risk variables in AA and tailor therapies accordingly, infection risk. Research has implicated racial differences in
emphasizing the underlying mechanisms that influence gene expression as a factor for survival outcomes in non-
30
clinical outcomes in CMV management. kidney transplant settings, which could be extrapolated
to other organs for future study. As genetic testing for
There are several limitations to this study that merit medication administration is becoming more prevalent,
discussion. Despite the relatively large size of this cohort, the results of these tests could facilitate the identification of
multicenter and/or national registry data are required alleles associated with CMV serostatus and infection risk.
to substantiate the external validity of these findings.
Although we used the Scientific Registry of Transplant Another area for investigation is immunosenescence,
Recipients (SRTR) data to validate these CMV D+/R− which may contribute to the increased risk of infection
trends within the same period, further rigorous research in AAs. This phenomenon may provide an environment
31
is warranted. The retrospective nature of the present for new infections and reactivation of latent CMV,
study precludes causal inference due to concerns related warranting further research.
to unmeasured and residual confounding. Nevertheless, 5. Conclusion
considerable effort and diligence were devoted to reducing
the occurrence of missing values through electronic and Although the incidence of CMV D+/R− serostatus has
manual chart abstraction and longitudinal modeling, which significantly increased in kidney transplantation over the
also ensured temporality in the relationships between risk past decade, AAs exhibit a 50% lower likelihood of being
Volume 11 Issue 2 (2025) 48 doi: 10.36922/jctr.24.00067