Page 66 - JCTR-11-4
P. 66
Journal of Clinical and
Translational Research AR-TAVR coaxiality assessment using 3DP
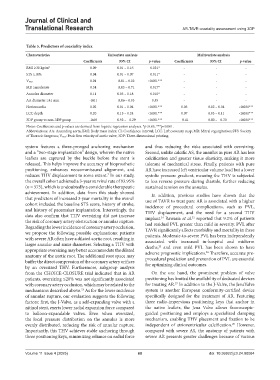
Table 5. Predictors of coaxiality index
Characteristics Univariate analysis Multivariate analysis
Coefficients 95% CI p‑value Coefficients 95% CI p‑value
BMI ≥30 kg/m 2 0.09 0.01 – 0.16 0.021* - - -
STS ≥10% 0.04 0.01 – 0.07 0.011* - - -
Vmax 0.01 −0.01 – 0.02 <0.001*** - - -
MR ≥moderate 0.34 −0.03 – 0.71 0.017* - - -
Annulus diameter 0.11 0.03 – 0.18 0.010* - - -
AA diameter ≥41 mm -0.01 −0.06 – 0.03 0.55 - - -
Horizocardia 0.02 0.01 – 0.04 <0.001*** 0.03 0.02 – 0.04 <0.001***
LCC depth 0.20 0.15 – 0.24 <0.001*** 0.07 0.03 – 0.11 <0.001***
3DP group vs non-3DP group -0.60 −0.92 – −0.29 <0.001*** −0.41 −0.80 – −0.30 <0.001***
Notes: Coefficients and p-values are derived from logistic regression analyses. *p<0.05, ***p<0.001.
Abbreviations: AA: Ascending aorta; BMI: Body mass index; CI: Confidence interval; LCC: Left coronary cusp; MR: Mitral regurgitation; STS: Society
of Thoracic Surgeons; Vmax: Peak flow velocity of aortic valve; 3DP: Three-dimensional printing.
system features a three-pronged anchoring mechanism and thus reducing the risks associated with oversizing.
and a “two-stage implantation” design, wherein the native Second, unlike calcific AS, the annulus in pure AR has less
leaflets are captured by the buckle before the stent is calcification and greater tissue elasticity, making it more
released. This helps improve the accuracy of bioprosthetic tolerant of mechanical stress. Finally, patients with pure
positioning, enhances neocommissural alignment, and AR have increased left ventricular volume load but a lower
reduces THV displacement to some extent. In our study, systolic pressure gradient, meaning the THV is subjected
7
the overall cohort achieved a 3-year survival rate of 93.95% to less reverse pressure during diastole, further reducing
(n = 575), which is undoubtedly a considerable therapeutic sustained tension on the annulus.
achievement. In addition, data from this study showed In addition, previous studies have shown that the
that predictors of increased 3-year mortality in the overall use of TAVR to treat pure AR is associated with a higher
cohort included the baseline STS score, history of stroke, incidence of procedural complications, such as PVL,
and history of pacemaker implantation. Interestingly, the THV displacement, and the need for a second THV
data also confirm that THV oversizing did not increase implant. Rawasia et al. reported that 9.2% of patients
24
22
the risk of coronary artery obstruction or annular rupture. had residual PVL greater than mild in severity. PVL after
Regarding the lower incidence of coronary artery occlusion, TAVR significantly affects morbidity and mortality in these
we propose the following possible explanations: patients patients. Moderate-to-severe PVL has been independently
with severe AR often have a dilated aortic root, resulting in
larger annular and sinus diameters. Selecting a THV with associated with increased in-hospital and midterm
deaths, and even mild PVL has been shown to have
25
appropriate oversizing may better accommodate the dilated adverse prognostic implications. Therefore, accurate pre-
26
anatomy of the aortic root. The additional root space may procedural prediction and prevention of PVL are essential
buffer the direct compression of the coronary artery orifices
by an oversized THV. Furthermore, subgroup analysis for optimizing clinical outcomes.
from the CHOICE-CLOSURE trial indicated that in AR On the one hand, the prominent problem of valve
patients, oversizing ≤20% was not significantly associated positioning has limited the availability of dedicated devices
with coronary artery occlusion, which may be related to the for treating AR. In addition to the J-Valve, the JenaValve
27
mechanisms described above. As for the lower incidence system is another European conformity-certified device
23
of annular rupture, our evaluation suggests the following specifically designed for the treatment of AR. Featuring
factors: first, the J-Valve, as a self-expanding valve with a three radio-impervious positioning keys that anchor in
nitinol stent, exerts lower radial expansion force compared the native leaflets, the Jena Valve allows fluoroscopic-
to balloon-expandable valves. Even when oversized, guided positioning and employs a specialized clamping
the local pressure distribution on the annulus is more mechanism, enabling THV placement and fixation to be
evenly distributed, reducing the risk of annular rupture. independent of atrioventricular calcification. However,
28
Importantly, this THV achieves stable anchoring through compared with severe AS, the anatomy of patients with
three positioning keys, minimizing reliance on radial force severe AR presents greater challenges because of various
Volume 11 Issue 4 (2025) 60 doi: 10.36922/jctr.24.00084