Page 47 - JCTR-9-4
P. 47
Ali et al. | Journal of Clinical and Translational Research 2023; 9(4): 261-264 263
disease status and are measured at an interval of 3 months for
the first 6 months after initial treatment, and then after 6 months
subsequently [11].
4. Conclusion
In conclusion, isolated raised serum alkaline phosphatase levels
should always be further investigated to rule out asymptomatic
patients. Management includes treatment with third-generation
bisphosphonates and pain control. Effective and time-sensitive
management can impart a huge difference in the outcome of
Paget’s disease.
Acknowledgments
None.
Funding
The authors received no financial support for the research,
authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest associated with the
material presented in this paper.
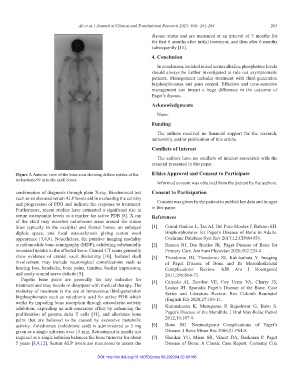
Figure 3. Anterior view of the bone scan showing diffuse uptake of the Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
technetium-99 m in the skull bones.
Informed consent was obtained from the patient by the authors.
confirmation of diagnosis through plain X-ray. Biochemical test Consent to Participation
such as an elevated serum ALP levels aid in evaluating the activity
and progression of PDB and indicate the response to treatment. Consent was given by the patient to publish her data and images
Furthermore, recent studies have estimated a significant rise in in this paper.
serum osteopontin levels as a marker for active PDB [8]. X-ray References
of the skull may manifest radiolucent areas around the suture
lines typically in the occipital and frontal bones, an enlarged [1] Corral-Gudino L, Tan AJ, Del Pino-Montes J, Ralston SH.
diploic space, and focal osteosclerosis giving cotton wool Bisphosphonates for Paget’s Disease of Bone in Adults.
appearance [3,8,9]. Nonetheless, the putative imaging modality Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2017;12:CD004956.
is radionuclide bone scintigraphy (MDP), exhibiting substantially [2] Rianon NJ, Des Bordes JK. Paget Disease of Bone for
increased uptake in the affected bone. Cranial CT scans generally Primary Care. Am Fam Physician 2020;102:224-8.
show evidence of cranial vault thickening [10]. Isolated skull [3] Theodorou DJ, Theodorou SJ, Kakitsubata Y. Imaging
involvement may include neurological complications such as of Paget Disease of Bone and Its Musculoskeletal
hearing loss, headache, bone pains, tinnitus, basilar impression, Complications: Review. AJR Am J Roentgenol
and rarely cranial nerve deficits [9]. 2011;196:S64-75.
Pagetic bone pains are generally the key indicator for [4] Caicedo AI, Escobar VE, Coy Urrea VA, Charry JS,
treatment and may recede or disappear with medical therapy. The Loaiza JH. Sporadic Paget’s Disease of the Bone. Case
mainstay of treatment is the use of intravenous third-generation Series and Literature Review. Rev Colomb Reumatol
bisphosphonates such as zoledronic acid for active PDB which (English Ed) 2020;27:103-11.
works by impeding bone resorption through osteoclastic activity
inhibition, expending an anti-cancerous effect by enhancing the [5] Karunakaran K, Murugesan P, Rajeshwar G, Babu S.
proliferation of gamma delta T cells [11], and alleviates bone Paget’s Disease of the Mandible. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol
pains that are believed to be caused by excessive metabolic 2012;16:107-9.
activity. Zoledronate (zoledronic acid) is administered as 5 mg [6] Bone HG. Nonmalignant Complications of Paget’s
given as a single infusion over 15 min. Retreatment is mostly not Disease. J Bone Miner Res 2006;21:P64-8.
required as a single infusion balances the bone turnover for about [7] Shankar YU, Misra SR, Vineet DA, Baskaran P. Paget
5 years [8,9,12]. Serum ALP levels are monitored to assess the Disease of Bone: A Classic Case Report. Contemp Clin
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18053/jctres.09.202304.22-00186