Page 113 - MI-2-1
P. 113
Microbes & Immunity Anti-mouse CXCR5 monoclonal antibody
A
B
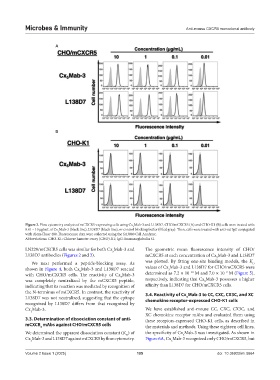
Figure 2. Flow cytometry analysis of mCXCR5-expressing cells using Cx Mab-3 and L138D7. CHO/mCXCR5 (A) and CHO-K1 (B) cells were treated with
5
0.01 – 10 µg/mL of Cx Mab-3 (black line), L138D7 (black line), or control blocking buffer (filled gray). Then, cells were treated with anti-rat IgG conjugated
5
with Alexa Fluor 488. Fluorescence data were collected using the SA3800 Cell Analyzer.
Abbreviations: CHO-K1: Chinese hamster ovary (CHO)-K1; IgG: Immunoglobulin G.
LN229/mCXCR5 cells was similar for both Cx Mab-3 and The geometric mean fluorescence intensity of CHO/
5
L138D7 antibodies (Figures 2 and 3). mCXCR5 at each concentration of Cx Mab-3 and L138D7
5
We next performed a peptide-blocking assay. As was plotted. By fitting one-site binding models, the K
D
shown in Figure 4, both Cx Mab-3 and L138D7 reacted values of Cx Mab-3 and L138D7 for CHO/mCXCR5 were
5
5
−10
−9
with CHO/mCXCR5 cells. The reactivity of Cx Mab-3 determined as 7.2 × 10 M and 7.0 × 10 M (Figure 5),
5
was completely neutralized by the mCXCR5 peptide, respectively, indicating that Cx Mab-3 possesses a higher
5
indicating that its reaction was mediated by recognition of affinity than L138D7 for CHO/mCXCR5 cells.
the N-terminus of mCXCR5. In contrast, the reactivity of 3.4. Reactivity of Cx Mab-3 to CC, CXC, CX3C, and XC
L138D7 was not neutralized, suggesting that the epitope chemokine receptor-expressed CHO-K1 cells
5
recognized by L138D7 differs from that recognized by
Cx Mab-3. We have established anti-mouse CC, CXC, CX3C, and
5
XC chemokine receptor mAbs and evaluated them using
3.3. Determination of dissociation constant of anti- these receptors-expressed CHO-K1 cells, as described in
mCXCR mAbs against CHO/mCXCR5 cells
5 the materials and methods. Using these eighteen cell lines,
We determined the apparent dissociation constant (K ) of the specificity of Cx Mab-3 was investigated. As shown in
D
5
Cx Mab-3 and L138D7 against mCXCR5 by flow cytometry. Figure 6A, Cx Mab-3 recognized only CHO/mCXCR5, but
5
5
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2025) 105 doi: 10.36922/mi.5664