Page 59 - MI-2-3
P. 59
Microbes & Immunity Understanding lung development, health, and diseases
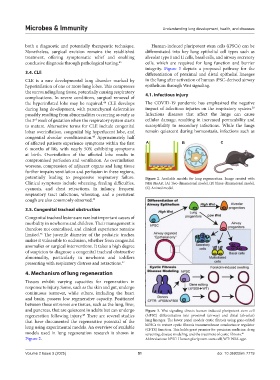
both a diagnostic and potentially therapeutic technique. Human-induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) can be
Nonetheless, surgical excision remains the established differentiated into key lung epithelial cell types such as
treatment, offering symptomatic relief and enabling alveolar type I and II cells, basal cells, and airway secretory
conclusive diagnosis through pathological testing. 43 cells, which are required for lung function and barrier
integrity. Figure 3 depicts a proposed pathway for the
3.4. CLE differentiation of proximal and distal epithelial lineages
CLE is a rare developmental lung disorder marked by in the lung after activation of human iPSC-derived airway
hyperinflation of one or more lung lobes. This compresses epithelium through Wnt signaling.
the surrounding lung tissue, potentially causing respiratory 4.1. Infectious injury
complications. In severe conditions, surgical removal of
the hyperinflated lobe may be required. CLE develops The COVID-19 pandemic has emphasized the negative
44
50
during lung development, with parenchymal deformities impact of infectious injuries on the respiratory system.
possibly resulting from abnormalities occurring as early as Infectious diseases that affect the lungs can cause
the 3 week of gestation when the respiratory system starts cellular damage, resulting in increased permeability and
rd
to mature. Alternative terms for CLE include congenital susceptibility to secondary infections. While the lungs
lobar overinflation, congenital big hyperlucent lobe, and remain quiescent during homeostasis, infections such as
congenital alveolar overdistension. Approximately half
45
of affected patients experience symptoms within the first A B C
6 months of life, with nearly 50% exhibiting symptoms
at birth. Overinflation of the affected lobe results in
compromised perfusion and ventilation. As overinflation
worsens, compression of adjacent organs and lung tissue
further impairs ventilation and perfusion in these regions,
potentially leading to progressive respiratory failure. Figure 2. Available models for lung regeneration. Image created with
Clinical symptoms include wheezing, feeding difficulties, NIH BioArt. (A) Two-dimensional model, (B) Three-dimensional model,
cyanosis, and chest retractions. In infancy, frequent (C) Animal model.
respiratory tract infections, wheezing, and a persistent
cough are also commonly observed. 44
3.5. Congenital tracheal obstruction
Congenital tracheal lesions are rare but important causes of
morbidity in newborns and children. Their management is
therefore not centralized, and clinical experience remains
limited. The juvenile diameter of the pediatric trachea
46
makes it vulnerable to occlusion, whether from congenital
anomalies or surgical interventions. It takes a high degree
of suspicion to diagnose a congenital tracheal obstructive
abnormality, particularly in newborns and toddlers
presenting with respiratory distress and retractions. 47
4. Mechanism of lung regeneration
Tissues exhibit varying capacities for regeneration in
response to injury. Some, such as the skin and gut, undergo
continuous turnover, while others, including the heart
and brain, possess low regenerative capacity. Positioned
between these extremes are tissues, such as the lung, liver,
and pancreas, that are quiescent in adults but can undergo Figure 3. Wnt signaling directs human induced pluripotent stem cell
regeneration following injury. There are several studies (hiPSC) differentiation into proximal (airway) and distal (alveolar)
48
that have documented the regenerative potential of the lung lineages. The lower panel models cystic fibrosis using gene-edited
lung using experimental models. An overview of available hiPSCs to restore cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator
(CFTR) function. This holds great promise for precision medicine, drug
models used in lung regeneration research is shown in screening, disease modeling, and the treatment of cystic fibrosis. 49
Figure 2. Abbreviations: hPSC: Human pluripotent stem cell; WT: Wild-type.
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2025) 51 doi: 10.36922/mi.7719