Page 125 - MI-2-4
P. 125
Microbes & Immunity Isolation and identification of PEDV strain CHN-CQ-2021
sustainable development of the global swine industry. and intestinal pathological tissues, were collected,
Notably, the emergence of a PEDV variant strain in China successful viral isolation was exclusively achieved from
in 2010 resulted in substantial economic losses to pig fresh intestinal samples of diarrheic piglets. This finding
29
farms nationwide, primarily due to its ability to evade suggests that intestinal pathological tissues with higher
the immune protection conferred by existing vaccines. virus loads are easier to isolate viruses compared to
30
Therefore, research on the biological characteristics of anal swabs. Low viral titers resulting from suboptimal
currently circulating PEDV strains is crucial for assessing sample collection, transportation, or storage conditions
the efficacy of existing vaccines and guiding vaccine may significantly hinder isolation efficiency. In addition,
development strategies. In this study, we isolated a highly unfiltered samples, which were not sterilized by filtration,
pathogenic PEDV strain from the intestines of piglets yielded higher isolation rates, likely because filtration
with diarrhea. The genome of the isolated PEDV strain removed a substantial number of viral particles. However,
(CHN-CQ-2021) and pathogenicity were analyzed, which unfiltered samples required supplementation with
will help to understand the biological characteristics of high concentrations of antibiotics to suppress bacterial
prevalent PEDV strains in China. contamination and maintain cell viability. After three
serial passages in Vero cells, the isolated virus induced
The Vero cell line, derived from the kidney of an significant CPE, which was subsequently confirmed as
African green monkey in 1962, has been widely used PEDV by indirect IFA and TEM observation. A viral
31
for the isolation of coronaviruses, such as PEDV and growth curve generated by infecting Vero cells with
SARS-CoV-2. 21,27,32 In this study, we attempted to isolate CHN-CQ-2021 demonstrated robust viral proliferation,
PEDV from PEDV-positive clinical samples using Vero indicating its adaptability to this cell line and suitability
cells. Although multiple samples, including anal swabs for further mechanistic studies. Although we isolated the
PEDV CHN-CQ-2021 strain, it is noteworthy that many
clinical samples failed to yield viable virus. Our findings
suggest that viral load in samples is a critical determinant
for successful isolation. To improve isolation efficiency,
pre-enrichment of viruses by passaging clinical materials
through susceptible piglets before cell culture inoculation
is strongly recommended. 26
To characterize the virus isolate, the whole genome of
the CHN-CQ-2021 strain was sequenced and analyzed.
Phylogenetic analysis revealed that the complete genomes
of all PEDV strains retrieved from GenBank share high
sequence similarity. Notably, the CHN-CQ-2021 strain
isolated in Chongqing exhibited the closest genetic
homology with PEDV strains AJ1102 and GD-1, which
were previously isolated in Jiangsu and Guangdong,
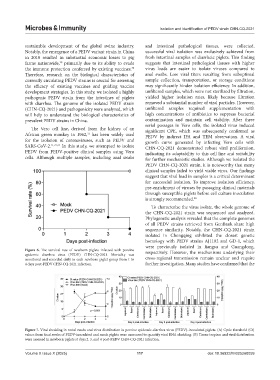
Figure 6. The survival rate of newborn piglets infected with porcine respectively. However, the mechanisms underlying their
epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV) CHN-CQ-2021. Mortality was
monitored and recorded daily in each newborn piglet group from 1 to cross-regional transmission remain unclear and require
4 days post-PEDV CHN-CQ-2021 infection. further investigation. Many studies have confirmed that the
Figure 7. Viral shedding in rectal swabs and virus distribution in porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV)-inoculated piglets. (A) Cycle threshold (Ct)
values from fecal swabs of PEDV-inoculated and mock piglets were measured to quantify viral RNA shedding. (B) Tissue tropism and viral distribution
were assessed in newborn piglets at days 2, 3, and 4 post-PEDV CHN-CQ-2021 infection.
Volume X Issue X (2025) 117 doi: 10.36922/MI025260059