Page 126 - MI-2-4
P. 126
Microbes & Immunity Isolation and identification of PEDV strain CHN-CQ-2021
A B
C D E
F G H
I J K
L M N
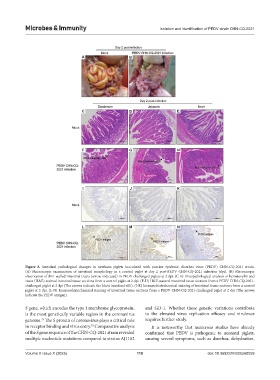
Figure 8. Intestinal pathological changes in newborn piglets inoculated with porcine epidemic diarrhea virus (PEDV) CHN-CQ-2021 strain.
(A) Macroscopic examination of intestinal morphology in a control piglet at day 2 post-PEDV CHN-CQ-2021 infection (dpi). (B) Macroscopic
observation of thin-walled intestinal tracts (arrow-indicated) in PEDV-challenged piglets at 2 dpi. (C-E) Histopathological analysis of hematoxylin and
eosin (H&E)-stained intestinal tissue sections from a control piglet at 2 dpi. (F-H) H&E-stained intestinal tissue sections from a PEDV CHN-CQ-2021-
challenged piglet at 2 dpi (The arrows indicate the blunt intestinal villi). (I-K) Immunohistochemical staining of intestinal tissue sections from a control
piglet at 2 dpi. (L-N) Immunohistochemical staining of intestinal tissue sections from a PEDV CHN-CQ-2021-challenged piglet at 2 dpi (The arrows
indicate the PEDV antigen).
S gene, which encodes the type I membrane glycoprotein, and GD-1. Whether these genetic variations contribute
is the most genetically variable region in the coronavirus to the elevated virus replication efficacy and virulence
genome. The S protein of coronavirus plays a critical role requires further study.
33
in receptor binding and virus entry. Comparative analysis It is noteworthy that numerous studies have already
33
of the S gene sequence of the CHN-CQ-2021 strain revealed confirmed that PEDV is pathogenic to neonatal piglets,
multiple nucleotide mutations compared to strains AJ1102 causing several symptoms, such as diarrhea, dehydration,
Volume X Issue X (2025) 118 doi: 10.36922/MI025260059