Page 15 - MSAM-1-4
P. 15
Materials Science in Additive Manufacturing Y O influence in heat-treated LPBF IN718 composite
2 3
The grain sizes of the printed samples after different ± 4.1 µm (after aging). On the other hand, the grain size of
stages of heat treatment are listed in Table 6. It can be seen the monolithic sample increases from 18.9 ± 1.9 µm to 23.8
that the grain size of the as-printed IN718/Y O composite ± 8.2 µm after solutionizing and decreases to 18.9 ± 4.4 µm
3
2
sample is slightly larger than that of the as-printed after aging. It should be noted that both samples achieve
monolithic IN718 sample. The limited grain refinement grain refinement after aging but the effect is stronger in the
effect in the as-printed IN718/Y O composite sample is the Y O -reinforced sample as the grain size decreases by 26.9%
2
3
2
3
result of the low wettability between the Y O nanoparticles compared to 20.6% in the monolithic sample. This suggests
2
3
and the IN718 matrix, which makes them not effective as that both the existing carbonitride precipitates and the newly
nucleation sites . However, after solutionizing and aging, form nano-sized Y-Ti-O precipitates contribute to the grain
[35]
there is an increase in equiaxed grains formation in the refinement. These precipitates aid the grain recrystallization
Y O -reinforced sample after heat treatment as shown in at high temperature by acting as nucleation centers. As
3
2
Figure 7C and D. Due to this, the average grain size of the such, due to the absence of the Y-Ti-O precipitates in the
Y O -reinforced sample decreases from 19.1 ± 3.1 (before monolithic samples, the carbonitride precipitates alone
2
3
heat treatment) to 17.1 ± 7.2 µm (after solutionizing) to 12.5 are not enough to suppress grain growth due to the high
temperature during solutionizing treatment. This results
[36]
Table 6. Grain sizes (µm) of the printed samples at different in a bigger grain size in the solutionized monolithic sample.
stages of heat treatment
3.3. Mechanical properties of heat-treated IN718
Reinforcement As‑printed 1075°C 1075°C composites
solutionized solutionized+aged
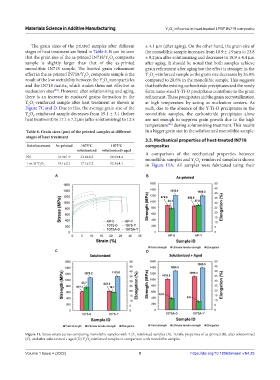
Nil 18.9±1.9 23.8±8.2 18.9±4.4 A comparison of the mechanical properties between
monolithic samples and Y O -reinforced samples is shown
2
3
1 wt.% Y O 3 19.1±3.1 17.1±7.2 12.5±4.1 in Figure 11A. All samples were fabricated using their
2
A B
C D
Figure 11. Stress-strain curves comparing monolithic samples with Y O -reinforced samples (A). Tensile properties of as-printed (B), after solutionized
2
3
(C), and after solutionized + aged (D) Y O -reinforced samples in comparison with monolithic samples.
2
3
Volume 1 Issue 4 (2022) 9 https://doi.org/10.18063/msam.v1i4.25