Page 48 - MSAM-1-4
P. 48
Materials Science in Additive Manufacturing Acoustic performances of SC lattices fabricated by DLP
A B
d
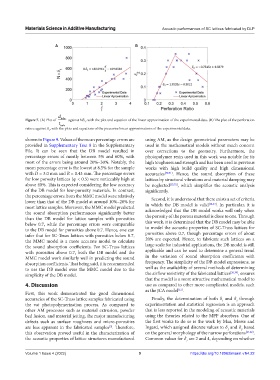
Figure 7. (A) Plot of tube against Nδ , with the plot and equation of the linear approximation of the experimental data. (B) The plot of the perforation
t tube
1
ratio ε against δ , with the plots and equations of the piecewise linear approximations of the experimental data.
2
shown in Figure 9. Values of the mean percentage errors are using AM, as the design geometrical parameters may be
provided in Supplementary Text 8 in the Supplementary used in the mathematical models without much concern
File. It can be seen that the DB model resulted in over corrections to the geometry. Furthermore, the
percentage errors of mostly between 5% and 60%, with photopolymer resin used in this work was notable for its
most of the errors being around 20%–30%. Notably, the high toughness and strength and has been used in previous
mean percentage error is the lowest at 8.5% for the sample works with high build quality and high dimensional
with D = 3.0 mm and R = 0.43 mm. The percentage errors accuracies [30,31] . Hence, the sound absorption of these
for low porosity lattices (φ < 0.5) were noticeably high at lattices by structural vibrations and material damping may
above 40%. This is expected considering the low accuracy be neglected [12,32] , which simplifies the acoustic analysis
of the DB model for low-porosity materials. In contrast, significantly.
the percentage errors from the MMC model were relatively Second, it is understood that there exists a set of criteria
lower than that of the DB model at around 10%–20% for in which the DB model is valid [12,33] . In particular, it is
most lattice samples. Moreover, the MMC model predicted
the sound absorption performances significantly better acknowledged that the DB model works well only when
than the DB model for lattice samples with porosities the porosity of the porous material is close to one. Through
below 0.7, while the percentage errors were comparable this work, it is determined that the DB model may be able
to the DB model for porosities above 0.7. Hence, one can to model the acoustic properties of SC-Truss lattices for
infer that for SC-Truss lattices with porosities below 0.7, porosities above 0.7, though percentage errors of about
the MMC model is a more accurate model to calculate 20% are expected. Hence, to fabricate such lattices on a
the sound absorption coefficients. For SC-Truss lattices large scale for industrial applications, the DB model is still
with porosities above 0.7, both the DB model and the applicable and can be used to determine a general trend
MMC model work similarly well in predicting the sound in the variation of sound absorption coefficients with
absorption coefficients. That being said, it is recommended frequency. The simplicity of the DB model expressions, as
to use the DB model over the MMC model due to the well as the availability of several methods of determining
simplicity of the DB model. the airflow resistivity of the fabricated lattices [26,34] , ensures
that the model is a more attractive mathematical model to
4. Discussion use as compared to other more complicated models, such
as the JCA model .
[12]
First, this work demonstrated the good dimensional
accuracies of the SC-Truss lattice samples fabricated using Finally, the determination of both δ and δ through
1
2
the vat photopolymerization process. As compared to experimentation and statistical regression is an approach
other AM processes such as material extrusion, powder that is less reported in the modeling of acoustic materials
bed fusion, and material jetting, the major manufacturing using the theories related to the MPP absorbers. One of
defects such as surface roughness and micro-porosities the first works to do so is the work by Maa, Morse and
are less apparent in the fabricated samples . Therefore, Ingard, which assigned discrete values to δ and δ based
[5]
1
2
this observation proved useful in the characterization of on the general morphology of the narrow perforations [21,22] .
the acoustic properties of lattice structures manufactured Common values for δ are 2 and 4, depending on whether
1
Volume 1 Issue 4 (2022) 9 https://doi.org/10.18063/msam.v1i4.22