Page 49 - MSAM-1-4
P. 49
Materials Science in Additive Manufacturing Acoustic performances of SC lattices fabricated by DLP
A B
C D
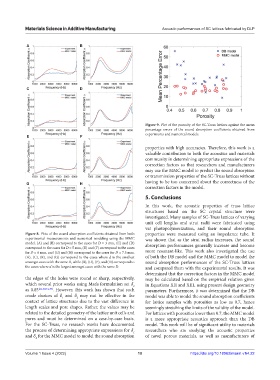
Figure 9. Plot of the porosity of the SC-Truss lattices against the mean
percentage errors of the sound absorption coefficients obtained from
E F experiments and numerical models.
properties with high accuracies. Therefore, this work is a
valuable contribution to both the acoustics and materials
community in determining appropriate expressions of the
correction factors so that researchers and manufacturers
may use the MMC model to predict the sound absorption
or transmission properties of the SC-Truss lattices without
G H having to be too concerned about the correctness of the
correction factors in the model.
5. Conclusions
In this work, the acoustic properties of truss lattice
structures based on the SC crystal structure were
investigated. Many samples of SC-Truss lattices of varying
unit cell lengths and strut radii were fabricated using
vat photopolymerization, and their sound absorption
Figure 8. Plots of the sound absorption coefficients obtained from both properties were measured using an impedance tube. It
experimental measurements and numerical modeling using the MMC was shown that as the strut radius increases, the sound
model. (A) and (B) correspond to the cases for D = 3 mm, (C) and (D) absorption performances generally increase and become
correspond to the cases for D = 5 mm, (E) and (F) correspond to the cases
for D = 6 mm, and (G) and (H) correspond to the cases for D = 7.5 mm. more resonant-like. This work also investigated the use
(A), (C), (E), and (G) correspond to the cases where d is the smallest of both the DB model and the MMC model to model the
amongst cases with the same D, while (B), (D), (F), and (H) correspond to sound absorption performances of the SC-Truss lattices
the cases where d is the largest amongst cases with the same D. and compared them with the experimental results. It was
determined that the correction factors in the MMC model
the edges of the holes were round or sharp, respectively, may be calculated based on the empirical relation given
which several prior works using Maa’s formulation set δ in Equations XII and XIII, using present design geometry
2
as 0.85 [21,30,31,35] . However, this work has shown that such parameters. Furthermore, it was determined that the DB
crude choices of δ and δ may not be effective in the model was able to model the sound absorption coefficients
2
1
context of lattice structures due to the vast difference in for lattice samples with porosities as low as 0.7, hence
length scales and pore shapes. Rather, the values may be seemingly stretching the limits of the validity of the model.
related to the detailed geometry of the lattice unit cells and For lattices with porosities lower than 0.7, the MMC model
pores and must be determined on a case-by-case basis. is a more appropriate acoustics approach than the DB
For the SC-Truss, no research works have documented model. This work will be of significant utility to materials
the process of determining appropriate expressions for δ researchers who are studying the acoustic properties
1
and δ for the MMC model to model the sound absorption of novel porous materials, as well as manufacturers of
2
Volume 1 Issue 4 (2022) 10 https://doi.org/10.18063/msam.v1i4.22