Page 36 - MSAM-2-1
P. 36
Materials Science in Additive Manufacturing 3D-printed nozzle for 3D bioprinting
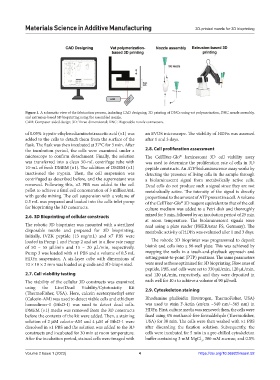
Figure 1. A schematic view of the fabrication process, including CAD designing, 3D printing of DNCs using vat polymerization, DNC nozzle assembly,
and extrusion-based 3D bioprinting using the assembled nozzle.
CAD: Computer-aided design; 3D: Three-dimensional; DNC: Disposable nozzle connectors.
of 0.05% trypsin-ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (×1) was an EVOS microscope. The viability of HDFn was assessed
added to the cells to detach them from the surface of the after 1 and 3 days.
flask. The flask was then incubated at 37°C for 5 min. After
the incubation period, the cells were examined under a 2.8. Cell proliferation assessment
microscope to confirm detachment. Finally, the solution The CellTiter-Glo luminescent 3D cell viability assay
®
was transferred into a clean 50-mL centrifuge tube with was used to determine the proliferation rate of cells in 3D
10-mL of fresh DMEM (×1). The addition of DMEM (×1) peptide constructs. An ATP bioluminescence assay works by
inactivated the trypsin. Then, the cell suspension was detecting the presence of living cells in the sample through
centrifuged as described before, and the supernatant was a bioluminescent signal from metabolically active cells.
removed. Following this, ×2 PBS was added to the cell Dead cells do not produce such a signal since they are not
pellet to achieve a final cell concentration of 3 million/mL metabolically active. The intensity of the signal is directly
with gentle mixing. The cell suspension with a volume of proportional to the amount of ATP present in a cell. A volume
0.5 mL was prepared and loaded into the cells inlet pump of the CellTiter-Glo 3D reagent equivalent to that of the cell
®
for bioprinting the 3D constructs. culture medium was added to a Petri dish and thoroughly
2.6. 3D Bioprinting of cellular constructs mixed for 5 min, followed by an incubation period of 25 min
at room temperature. The bioluminescent signals were
The robotic 3D bioprinter was mounted with a sterilized read using a plate reader (PHERAstar FS, Germany). The
disposable nozzle and prepared for 3D bioprinting. metabolic activity of HDFn was evaluated after 1 and 3 days.
Initially, IVZK peptide (13 mg/mL) and ×7 PBS were
loaded in Pump 1 and Pump 2 and set to a flow rate range The robotic 3D bioprinter was programmed to deposit
of 50 – 55 µL/min and 15 – 20 µL/min, respectively. bioink and cells into a 96-well plate. This was achieved by
Pump 3 was loaded with ×1 PBS and a volume of 0.5 mL mapping the wells in a teach-and-playback approach and
HDFn suspension. A six-layer cube with dimensions of setting point-to-point (PTP) positions. The same parameters
10 × 10 × 2 mm was loaded as g-code and 3D-bioprinted. were used as those optimized for 3D bioprinting. Flow rates of
peptide, PBS, and cells were set to 330 µL/min, 120 µL/min,
2.7. Cell viability testing and 120 µL/min, respectively, and they were deposited in
The viability of the cellular 3D constructs was examined each well for 10 s to achieve a volume of 90 µl/well.
using the Live/Dead Viability/Cytotoxicity Kit 2.9. Cytoskeleton staining
(ThermoFisher, USA). Here, calcein acetoxymethyl ester
(Calcein-AM) was used to detect viable cells and ethidium Rhodamine phalloidin (Invitrogen, ThermoFisher, USA)
homodimer-I (EthD-I) was used to detect dead cells. was used to stain F-Actin (ex/em ~540 nm/~565 nm) in
DMEM (×1) media was removed from the 3D constructs HDFn. First, culture media was removed; then, the cells were
before the contents of the kit were added. Then, a staining fixed using 4% methanol-free formaldehyde (Thermofisher,
solution of 2 µM calcein-AM and 4 µM of EthD-1 were USA) for 30 min. The cells were then washed with ×1 PBS
dissolved in ×1 PBS and the solution was added to the 3D after discarding the fixation solution. Subsequently, the
constructs and incubated for 30 min at room temperature. cells were incubated for 5 min in a pre-chilled cytoskeleton
After the incubation period, stained cells were imaged with buffer containing 3 mM MgCl , 300 mM sucrose, and 0.5%
2
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2023) 4 https://doi.org/10.36922/msam.52