Page 53 - MSAM-3-1
P. 53
Materials Science in Additive Manufacturing Adhesion study for multi-material 3D printing
fracture characteristics (Figure 4D) between the cleanly demonstrated significantly higher interlaminar adhesive
separated samples and those with mechanical interlocks strength than the unmodified cPLA TPU coupons.
underline the influence of interface modifications on This suggests that the modifications introduce a stronger
interlaminar adhesion strength and failure behavior. adhesive force between cPLA and TPU, which is sufficient
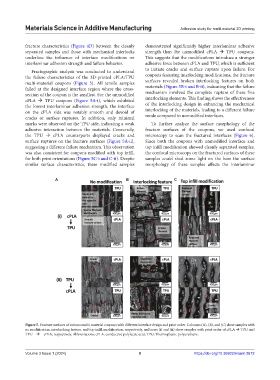
Fractographic analysis was conducted to understand to initiate cracks and surface rupture upon failure. For
the failure characteristics of the 3D-printed cPLA/TPU coupons featuring interlocking modifications, the fracture
multi-material coupons (Figure 5). All tensile samples surfaces revealed broken interlocking features on both
failed at the designed interface region where the cross- materials (Figure 5B-i and B-ii), indicating that the failure
section of the coupon is the smallest. For the unmodified mechanism involved the complete rupture of these fine
cPLA TPU coupons (Figure 5A-i), which exhibited interlocking elements. This finding shows the effectiveness
the lowest interlaminar adhesion strength, the interface of the interlocking design in enhancing the mechanical
on the cPLA side was notably smooth and devoid of interlocking of the materials, leading to a different failure
cracks or surface ruptures. In addition, only minimal mode compared to unmodified interfaces.
marks were observed on the TPU side, indicating a weak To further analyze the surface morphology of the
adhesive interaction between the materials. Conversely, fracture surfaces of the coupons, we used confocal
the TPU cPLA counterparts displayed cracks and microscopy to scan the fractured interfaces (Figure 6).
surface ruptures on the fracture surfaces (Figure 5A-ii), Since both the coupons with unmodified interface and
suggesting a different failure mechanism. This observation top infill modification showed cleanly separated samples,
was also consistent for coupons modified with top infill, the confocal microscopy on the fractured surfaces of these
for both print orientations (Figure 5C-i and C-ii). Despite samples could shed some light on the how the surface
similar surface characteristics, these modified samples morphology of these samples affects the interlaminar
A B C
Figure 5. Fracture surfaces of various multi-material coupons with different interface design and print order. Columns (A), (B), and (C) show samples with
no modification, interlocking feature, and top infill modification, respectively, and rows (i) and (ii) show samples with print order of cPLA TPU and
TPU cPLA, respectively. Abbreviations: cPLA: conductive polylactic acid; TPU: Thermoplastic polyurethane.
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2024) 8 https://doi.org/10.36922/msam.2672