Page 51 - MSAM-3-1
P. 51
Materials Science in Additive Manufacturing Adhesion study for multi-material 3D printing
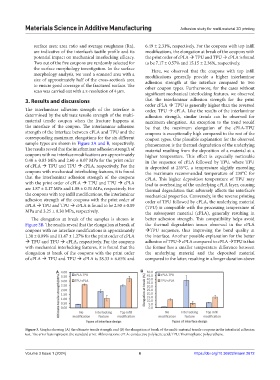
surface area: area ratio and average roughness (Ra), 6.49 ± 2.31%, respectively. For the coupons with top infill
are indicative of the interface’s tactile profile and its modifications, the elongation at break of the coupons with
potential impact on mechanical interlocking efficacy. the print order of cPLA TPU and TPU cPLA is found
Two out of the five coupons are randomly selected for to be 7.17 ± 0.57% and 15.15 ± 2.36%, respectively.
the surface morphology investigation. In the surface Here, we observed that the coupons with top infill
morphology analysis, we used a scanned area with a modifications generally provide a higher interlaminar
size of approximately half of the cross-section’s area adhesion strength at the interface compared to two
to ensure good coverage of the fractured surface. The other coupon types. Furthermore, for the cases without
scan was carried out with a z-resolution of 4 µm.
significant mechanical interlocking features, we observed
3. Results and discussions that the interlaminar adhesion strength for the print
order cPLA TPU is generally higher than the reversed
The interlaminar adhesion strength of the interface is order, TPU cPLA. Like the results of the interlaminar
determined by the ultimate tensile strength of the multi- adhesion strength, similar trends can be observed for
material tensile coupon when the fracture happens at maximum elongation. An exception to the trend would
the interface of the coupon. The interlaminar adhesion be that the maximum elongation of the cPLA-TPU
strength of the interface between cPLA and TPU and the coupons is exceptionally high compared to the rest of the
corresponding maximum elongations for the six different coupon types. One plausible explanation for the observed
sample types are shown in Figure 3A and B, respectively. phenomenon is the thermal degradation of the underlying
The results reveal that the interlaminar adhesion strength of material resulting from the deposition of a material at a
coupons with no interface modifications are approximately higher temperature. This effect is especially noticeable
0.40 ± 0.03 MPa and 2.60 ± 0.07 MPa for the print order in the sequence of cPLA followed by TPU, where TPU
of cPLA TPU and TPU cPLA, respectively. For the is deposited at 235°C, a temperature slightly exceeding
coupons with mechanical interlocking features, it is found the maximum recommended temperature of 230°C for
that the interlaminar adhesion strength of the coupons cPLA. This higher deposition temperature of TPU may
with the print order of cPLA TPU and TPU cPLA lead to overheating of the underlying cPLA layer, causing
are 1.87 ± 0.17 MPa and 1.08 ± 0.31 MPa, respectively. For thermal degradation that adversely affects the interface’s
the coupons with top infill modifications, the interlaminar mechanical properties. Conversely, in the reverse printing
adhesion strength of the coupons with the print order of order of TPU followed by cPLA, the underlying material
cPLA TPU and TPU cPLA is found to be 2.50 ± 0.09 (TPU) is compatible with the processing temperature of
MPa and 3.25 ± 0.30 MPa, respectively. the subsequent material (cPLA), generally resulting in
The elongation at break of the samples is shown in better adhesion strength. This compatibility helps avoid
Figure 3B. The results reveal that the elongation at break of the thermal degradation issues observed in the cPLA
coupons with no interface modifications is approximately TPU sequence, thus improving the bond quality at
1.30 ± 0.09% and 11.47 ± 1.27% for the print order of cPLA the interface. Another possible explanation for the better
TPU and TPU cPLA, respectively. For the coupons adhesion of TPU cPLA compared to cPLA TPU is that
with mechanical interlocking features, it is found that the the former has a smaller temperature difference between
elongation at break of the coupons with the print order the underlying material and the deposited material
of cPLA TPU and TPU cPLA is 38.33 ± 6.65% and compared to the latter, resulting in a longer duration above
A B
Figure 3. Graphs showing (A) the ultimate tensile strength and (B) the elongation at break of the multi-material tensile coupons in the interfacial adhesion
test. The error bars represent the standard error. Abbreviations: cPLA: conductive polylactic acid; TPU: Thermoplastic polyurethane.
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2024) 6 https://doi.org/10.36922/msam.2672