Page 123 - MSAM-3-2
P. 123
Materials Science in Additive Manufacturing Hybrid lattice structures design with AI
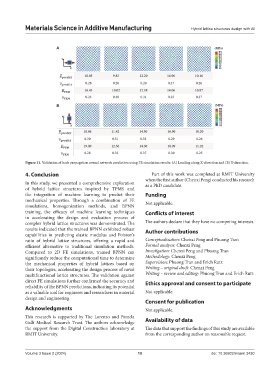
A
B
Figure 11. Validation of back propagation neural network prediction using FE simulation results: (A) Loading along X-direction and (B) Y-direction.
4. Conclusion Part of this work was completed at RMIT University
when the first author (Chenxi Peng) conducted his research
In this study, we presented a comprehensive exploration as a PhD candidate.
of hybrid lattice structures inspired by TPMS and
the integration of machine learning to predict their Funding
mechanical properties. Through a combination of FE Not applicable.
simulations, homogenization methods, and BPNN
training, the efficacy of machine learning techniques Conflicts of interest
in accelerating the design and evaluation process of
complex hybrid lattice structures was demonstrated. The The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
results indicated that the trained BPNN exhibited robust Author contributions
capabilities in predicting elastic modulus and Poisson’s
ratio of hybrid lattice structures, offering a rapid and Conceptualization: Chenxi Peng and Phuong Tran
efficient alternative to traditional simulation methods. Formal analysis: Chenxi Peng
Compared to 2D FE simulations, trained BPNN can Investigation: Chenxi Peng and Phuong Tran
significantly reduce the computational time to determine Methodology: Chenxi Peng
the mechanical properties of hybrid lattices based on Supervision: Phuong Tran and Erich Rutz
their topologies, accelerating the design process of novel Writing – original draft: Chenxi Peng
multifunctional lattice structures. The validation against Writing – review and editing: Phuong Tran and Erich Rutz
direct FE simulations further confirmed the accuracy and Ethics approval and consent to participate
reliability of the BPNN predictions, indicating its potential
as a valuable tool for engineers and researchers in material Not applicable.
design and engineering.
Consent for publication
Acknowledgments Not applicable.
This research is supported by The Lorenzo and Pamela Availability of data
Galli Medical Research Trust. The authors acknowledge
the support from the Digital Construction laboratory at The data that support the findings of this study are available
RMIT University. from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Volume 3 Issue 2 (2024) 10 doi: 10.36922/msam.3430