Page 121 - MSAM-3-2
P. 121
Materials Science in Additive Manufacturing Hybrid lattice structures design with AI
A B
C C D
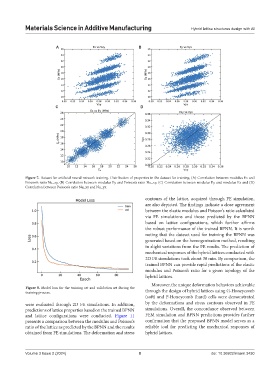
Figure 7. Dataset for artificial neural network training. Distribution of properties in the dataset for training. (A) Correlation between modulus Ex and
Poisson’s ratio Nu_xy, (B) Correlation between modulus Ey and Poisson’s ratio Nu_xy, (C) Correlation between modulus Ey and modulus Ex and (D)
Correlation between Poisson’s ratio Nu_xy and Nu_yx.
contours of the lattice, acquired through FE simulation,
are also depicted. The findings indicate a close agreement
between the elastic modulus and Poisson’s ratio calculated
via FE simulations and those predicted by the BPNN
based on lattice configurations, which further affirms
the robust performance of the trained BPNN. It is worth
noting that the dataset used for training the BPNN was
generated based on the homogenization method, resulting
in slight variations from the FE results. The prediction of
mechanical responses of the hybrid lattices conducted with
2D FE simulations took about 30 min. By comparison, the
trained BPNN can provide rapid predictions of the elastic
modulus and Poisson’s ratio for a given topology of the
hybrid lattices.
Moreover, the unique deformation behaviors achievable
Figure 8. Model loss for the training set and validation set during the
training process. through the design of hybrid lattices using G-Honeycomb
(soft) and P-Honeycomb (hard) cells were demonstrated
were evaluated through 2D FE simulations. In addition, by the deformations and stress contours observed in FE
predictions of lattice properties based on the trained BPNN simulations. Overall, the concordance observed between
and lattice configurations were conducted. Figure 11 FEM simulation and BPNN predictions provides further
presents a comparison between the modulus and Poisson’s confirmation that the proposed BPNN model serves as a
ratio of the lattice as predicted by the BPNN and the results reliable tool for predicting the mechanical responses of
obtained from FE simulations. The deformation and stress hybrid lattices.
Volume 3 Issue 2 (2024) 8 doi: 10.36922/msam.3430