Page 84 - MSAM-3-4
P. 84
Materials Science in Additive Manufacturing Impact resistance and porous structures
A B
C D
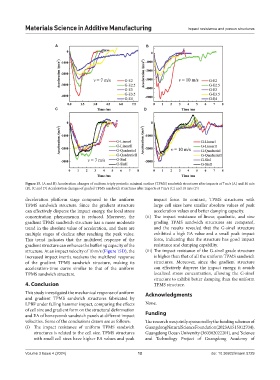
Figure 15. (A and B) Acceleration changes of uniform triply periodic minimal surface (TPMS) sandwich structures after impacts at 7 m/s (A) and 10 m/s
(B). (C and D) Acceleration changes of graded TPMS sandwich structures after impacts at 7 m/s (C) and 10 m/s (D)
deceleration platform stage compared to the uniform impact force. In contrast, TPMS structures with
TPMS sandwich structure. Since the gradient structure large cell sizes have smaller absolute values of peak
can effectively disperse the impact energy, the local stress acceleration values and better damping capacity.
concentration phenomenon is reduced. Moreover, the (ii) The impact resistance of linear, quadratic, and sine
gradient TPMS sandwich structure has a more moderate grading TPMS sandwich structures are compared,
trend in the absolute value of acceleration, and there are and the results revealed that the G-sineI structure
multiple stages of decline after reaching the peak value. exhibited a high EA value and a small peak impact
This trend indicates that the multilevel response of the force, indicating that the structure has good impact
gradient structure can enhance the buffering capacity of the resistance and damping capability.
structure. At an impact velocity of 10 m/s (Figure 15D), the (iii) The impact resistance of the G-sineI grade structure
increased impact inertia weakens the multilevel response is higher than that of all the uniform TPMS sandwich
of the gradient TPMS sandwich structure, making its structures. Moreover, since the gradient structure
acceleration-time curve similar to that of the uniform can effectively disperse the impact energy, it avoids
TPMS sandwich structure. localized stress concentration, allowing the G-sineI
structure to exhibit better damping than the uniform
4. Conclusion TPMS structure.
This study investigated the mechanical response of uniform Acknowledgments
and gradient TPMS sandwich structures fabricated by
LPBF under falling hammer impact, comparing the effects None.
of cell size and gradient form on the structural deformation
and EA of honeycomb sandwich panels at different impact Funding
velocities. Some of the conclusions drawn are as follows: The research was jointly sponsored by the funding schemes of
(i) The impact resistance of uniform TPMS sandwich Guangdong Natural Science Foundation (2023A1515012704),
structures is related to the cell size. TPMS structures Guangdong Ocean University (360302022201), and ‘Science
with small cell sizes have higher EA values and peak and Technology Project of Guangdong Academy of
Volume 3 Issue 4 (2024) 12 doi: 10.36922/msam.5729