Page 81 - MSAM-3-4
P. 81
Materials Science in Additive Manufacturing Impact resistance and porous structures
A B
C D
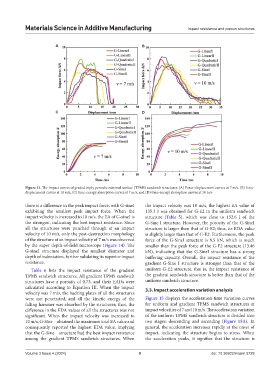
Figure 11. The impact curves of graded triply periodic minimal surface (TPMS) sandwich structures: (A) Force-displacement curves at 7 m/s, (B) force-
displacement curves at 10 m/s, (C) time-energy absorption curves at 7 m/s, and (D) time-energy absorption curves at 10 m/s
there is a difference in the peak impact force, with G-sineI the impact velocity was 10 m/s, the highest EA value of
exhibiting the smallest peak impact force. When the 135.3 J was obtained for G-E2 in the uniform sandwich
impact velocity is increased to 10 m/s, the EA of G-sineI is structure (Table 5), which was close to 132.6 J of the
the strongest, indicating the best impact resistance. Since G-Sine I structure. However, the porosity of the G-SineI
all the structures were punched through at an impact structure is larger than that of G-E2; thus, its EDA value
velocity of 10 m/s, only the post-destruction morphology is slightly larger than that of G-E2. Furthermore, the peak
of the structure at an impact velocity of 7 m/s was observed force of the G-SineI structure is 8.5 kN, which is much
by the super depth-of-field microscope (Figure 14). The smaller than the peak force of the G-E2 structure (13.46
G-sineI structure displayed the smallest diameter and kN), indicating that the G-SineI structure has a strong
depth of indentation, further validating its superior impact buffering capacity. Overall, the impact resistance of the
resistance. gradient G-Sine I structure is stronger than that of the
Table 6 lists the impact resistance of the gradient uniform G-E2 structure, that is, the impact resistance of
TPMS sandwich structures. All gradient TPMS sandwich the gradient sandwich structure is better than that of the
structures have a porosity of 0.73, and their EADs were uniform sandwich structure.
calculated according to Equation III. When the impact 3.3. Impact acceleration variation analysis
velocity was 7 m/s, the backing plates of all the structures
were not penetrated, and all the kinetic energy of the Figure 15 displays the acceleration-time variation curves
falling hammer was absorbed by the structures; thus, the for uniform and gradient TPMS sandwich structures at
difference in the EDA values of all the structures was not impact velocities of 7 and 10 m/s. The acceleration variation
significant. When the impact velocity was increased to of the uniform TPMS sandwich structure is divided into
10 m/s, G-SineⅠ obtained the maximum total EA value and two stages: descending and ascending (Figure 15A). In
consequently reported the highest EDA value, implying general, the acceleration increases rapidly at the onset of
that the G-SineⅠ structure had the best impact resistance impact, indicating the structure begins to stress. When
among the gradient TPMS sandwich structures. When the acceleration peaks, it signifies that the structure is
Volume 3 Issue 4 (2024) 9 doi: 10.36922/msam.5729