Page 108 - OR-1-2
P. 108
and specific tumor evolution. 6,7,12-14 Thus, neither cancer colorectal, liver, pancreatic, breast, and gastric cancers.
16
cell lines grown in culture media nor tumor cells grown In this review, we summarize and outline the latest
in mouse models can accurately and perfectly replicate developments in the application of organoid technology
and simulate the diversity and complexity of tumors in the and clinical cancer research.
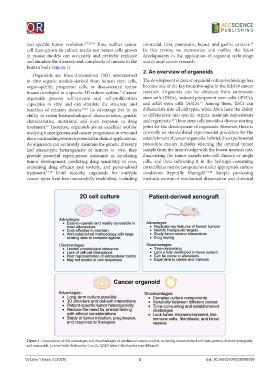
human body (Figure 1).
2. An overview of organoids
Organoids are three-dimensional (3D) miniaturized
in vitro organic models derived from human stem cells, The development of cancer organoid culture technology has
organ-specific progenitor cells, or disassociated tumor become one of the key breakthroughs in the field of cancer
tissues developed in a specific 3D culture system. Cancer research. Organoids can be obtained from embryonic
15
organoids possess self-renewal and self-proliferation stem cells (ESCs), induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs),
19
capacities in vitro and can simulate the structure and and adult stem cells (ASCs). Among them, ESCs can
function of primary tissues. 15,16 Its advantage lies in its differentiate into all cell types, while ASCs have the ability
ability to retain histopathological characteristics, genetic to differentiate into specific organs, maintain homeostasis
20
characteristics, mutations, and even response to drug and regenerate. These stem cells provide a diverse starting
treatment. Therefore, organoids are an excellent tool for point for the development of organoids. However, there is
17
studying tumorigenesis and cancer progression in vitro and currently no standardized experimental procedure for the
show outstanding research potential in clinical applications. establishment of cancer organoids. In brief, the experimental
As organoids can accurately maintain the genetic diversity procedure mainly includes selecting the optimal tumor
and phenotypic heterogeneity of tumors in vivo, they sample from the tumor’s edge with the lowest necrosis rate,
provide powerful experimental assistance in simulating dissociating the tumor sample into cell clusters or single
tumor development, predicting drug sensitivity in vivo, cells, and then cultivating it in the hydrogel containing
evaluating drug efficacy and toxicity, and personalized extracellular matrix components under appropriate culture
treatment. 17,18 Until recently, organoids for multiple conditions (typically Matrigel). 19,20 Sample processing
cancer types have been successfully established, including methods consist of mechanical dissociation and chemical
Figure 1. Comparison of the advantages and disadvantages of preclinical cancer models, including immortalized cell lines, patient-derived xenografts,
and organoids. Created with BioRender. Cao, K. (2025) https://BioRender.com/48hmj45.
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2025) 2 doi: 10.36922/OR025050008