Page 109 - OR-1-2
P. 109
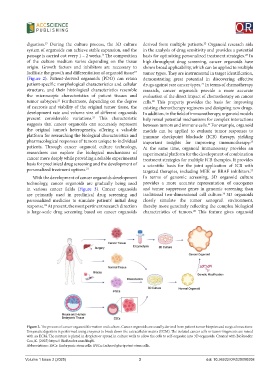
digestion. During the culture process, the 3D culture derived from multiple patients. Organoid research aids
22
15
system of organoids can achieve stable expansion, and the in the analysis of drug sensitivity and provides a potential
15
passage is carried out every 1 – 2 weeks. The composition basis for optimizing personalized treatment strategies. In
23
of the culture medium varies depending on the tissue high-throughput drug screening, cancer organoids have
origin. Growth factors and inhibitors are necessary to shown broad applicability, which can be applied to multiple
facilitate the growth and differentiation of organoid tissue tumor types. They are instrumental in target identification,
19
(Figure 2). Patient-derived organoids (PDO) can retain demonstrating great potential in discovering effective
patient-specific morphological characteristics and cellular drugs against rare cancer types. In terms of chemotherapy
23
structure, and their histological characteristics resemble research, cancer organoids provide a more accurate
the microscopic characteristics of patient tissues and evaluation of the direct impact of chemotherapy on cancer
tumor subtypes. Furthermore, depending on the degree cells. This property provides the basis for improving
21
20
of necrosis and viability of the original tumor tissue, the existing chemotherapy regimens and designing new drugs.
development rate and volume size of different organoids In addition, in the field of immunotherapy, organoid models
present considerable variations. This characteristic help reveal potential mechanisms for complex interactions
21
suggests that cancer organoids can accurately represent between tumors and immune cells. For example, organoid
24
the original tumor’s heterogeneity, offering a valuable models can be applied to evaluate tumor responses to
platform for researching the biological characteristics and immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) therapy, yielding
pharmacological responses of tumors unique to individual important insights for improving immunotherapy.
25
patients. Through cancer organoid culture technology, At the same time, organoid immunoassay provides an
researchers can explore the biological mechanisms of experimental platform for the development of combination
cancer more deeply while providing a reliable experimental treatment strategies for multiple ICB therapies. It provides
basis for preclinical drug screening and the development of a scientific basis for the joint application of ICB with
personalized treatment options. 21 targeted therapies, including MEK or BRAF inhibitors.
25
With the development of cancer organoids development In terms of genomic screening, 3D organoid culture
technology, cancer organoids are gradually being used provides a more accurate representation of oncogenes
in various cancer fields (Figure 3). Cancer organoids and tumor suppressor genes in genomic screening than
26
are primarily used in preclinical drug screening and traditional two-dimensional cell culture. 3D organoids
personalized medicine to simulate patients’ initial drug closely simulate the tumor xenograft environment,
response. At present, the most pertinent research direction thereby more genuinely reflecting the complex biological
22
is large-scale drug screening based on cancer organoids characteristics of tumors. This feature gives organoid
26
Figure 2. The process of cancer organoid formation and culture. Cancer organoids are usually derived from patient tumor biopsies and surgical resections.
Enzymatic digestion is performed using enzymes to break down the extracellular matrix (ECM). The isolated cancer cells or tumor fragments are mixed
with an ECM. The mixture is plated in droplets or spread in culture wells to allow the cells to self-organize into 3D organoids. Created with BioRender.
Cao, K. (2025) https:// BioRender.com/lfsqfti.
Abbreviations: ESCs: Embryonic stem cells; iPSCs: Induced pluripotent stem cells.
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2025) 3 doi: 10.36922/OR025050008