Page 32 - OR-1-2
P. 32
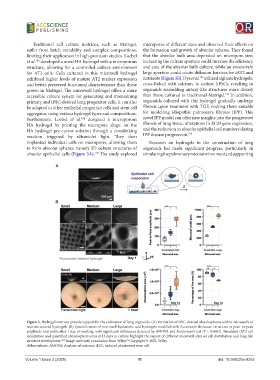
Traditional cell culture matrices, such as Matrigel, micropores of different sizes and observed their effects on
suffer from batch variability and complex compositions, the formation and growth of alveolar spheres. They found
limiting their application in high-precision studies. Loebel that the alveolar bulb area depended on micropore size;
et al. developed a novel HA hydrogel with a microporous increasing the culture aperture could increase the efficiency
104
structure, allowing for a controlled culture environment and area of the alveolar bulb culture, while an excessively
for AT2 cells. Cells cultured in this microwell hydrogel large aperture could create diffusion barriers for iAT2 and
105
exhibited higher levels of mature AT2 marker expression nutrients (Figure 3B). Dye et al. utilized alginate hydrogels,
and better-preserved functional characteristics than those cross-linked with calcium, to culture hPSCs, resulting in
grown in Matrigel. The microwell hydrogel offers a more organoids resembling airway-like structures more closely
105
accessible culture system for generating and maintaining than those cultured in traditional Matrigel. In addition,
primary and iPSC-derived lung progenitor cells. It can also organoids cultured with this hydrogel gradually undergo
be adapted to other epithelial progenitor cells and stem cell fibrosis upon treatment with TGF, making them suitable
aggregates, using various hydrogel types and compositions. for modelling idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). This
Furthermore, Loebel et al. designed a microporous novel IPF model can offer new insights into the progressive
104
HA hydrogel by printing the micropore shape on the fibrosis of lung tissue, alterations in ECM gene expression,
HA hydrogel pre-cursor solution through a crosslinking and the reduction in alveolar epithelial cell numbers during
reaction triggered by ultraviolet light. They then IPF disease progression. 105
implanted individual cells on micropores, allowing them Research on hydrogels in the construction of lung
to form alveolar spheres, namely 3D culture structures of organoids has made significant progress, particularly in
alveolar epithelial cells (Figure 3A). The study explored simulating the pulmonary microenvironment and supporting
104
A
B
Figure 3. Hydrogel matrices provide support for the cultivation of lung organoids. (A) Formation of iPSC-derived alveolospheres within microwells of
microstructured hydrogels. (B) Quantification of microwell hyaluronic acid hydrogels modified with fluorescein showcase variations in peak-to-peak
amplitude and width after 1 day of swelling, with significant differences detected by ANOVA and Bonferroni’s test (P < 0.0001). Simulated iAT2 cell
localization and quantified alveolosphere areas at 14 days in culture highlight the impact of different microwell sizes on cell distribution and lung-like
structure development. Image used with permission from Wiley, Copyright © 2022, Wiley.
24
104
Abbreviations: ANOVA: Analysis of variance; iPSC: Induced pluripotent stem cell.
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2025) 11 doi: 10.36922/or.8262