Page 52 - OR-1-2
P. 52
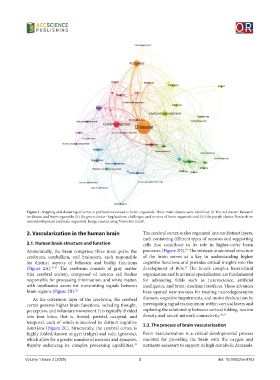
Figure 1. Mapping and clustering of terms in publications related to brain organoids. Three main clusters were identified: (i) The red cluster: Research
on disease and brain organoids; (ii) the green cluster: Applications, challenges, and reviews of brain organoids; and (iii) the purple cluster: Research on
neurodevelopment and brain organoids. Image created using Vosviewer 1.6.20.
2. Vascularization in the human brain The cerebral cortex is also organized into six distinct layers,
each containing different types of neurons and supporting
2.1. Human brain structure and function cells that contribute to its role in higher-order brain
34
Anatomically, the brain comprises three main parts: the processes (Figure 2D). The intricate anatomical structure
cerebrum, cerebellum, and brainstem, each responsible of the brain serves as a key to understanding higher
for distinct aspects of behavior and bodily functions cognitive functions and provides critical insights into the
35
(Figure 2A). 29-31 The cerebrum consists of gray matter development of BOs. The brain’s complex hierarchical
(the cerebral cortex), composed of neuron cell bodies organization and functional specialization are fundamental
responsible for processing information, and white matter, for advancing fields such as neuroscience, artificial
with myelinated axons for transmitting signals between intelligence, and brain–machine interfaces. These advances
brain regions (Figure 2B). 32 have opened new avenues for treating neurodegenerative
As the outermost layer of the cerebrum, the cerebral diseases, cognitive impairments, and motor dysfunction by
cortex governs higher brain functions, including thought, investigating signal transmission within cortical layers and
perception, and voluntary movement. It is typically divided exploring the relationship between cortical folding, neuron
into four lobes, that is, frontal, parietal, occipital, and density, and neural network connectivity. 36,37
temporal, each of which is involved in distinct cognitive 2.2. The process of brain vascularization
functions (Figure 2C). Structurally, the cerebral cortex is
highly folded, known as gyri (ridges) and sulci (grooves), Brain vascularization is a critical developmental process
which allow for a greater number of neurons and synapses, essential for providing the brain with the oxygen and
thereby enhancing its complex processing capabilities. nutrients necessary to support its high metabolic demands.
33
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2025) 3 doi: 10.36922/or.8162