Page 55 - OR-1-2
P. 55
is often associated with brain tumors such as glioblastoma basement membrane, provide additional structural support
(GBM). GBM, in particular, relies on extensive vascular and regulate blood flow, permeability, and vascular stability.
61
networks to support its rapid growth. Understanding the They are also crucial in controlling ECs’ proliferation
molecular and cellular mechanisms underlying brain and differentiation, playing a key role in establishing and
vascularization is crucial for gaining insights into brain preserving the integrity of the BBB. Astrocytes, whose
development and identifying potential therapeutic targets end-feet cover approximately 99% of the brain’s capillary
for vascular-related conditions. 62 surface, secrete signaling molecules that help maintain
BBB integrity and facilitate nutrient exchange between the
2.3. BBB
blood and neurons. Furthermore, the basement membrane,
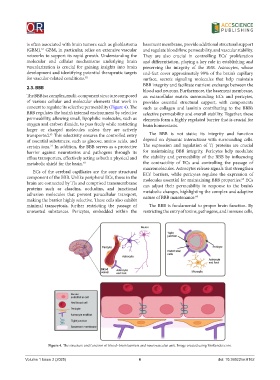
The BBB is a complex, multi-component structure composed an extracellular matrix surrounding ECs and pericytes,
of various cellular and molecular elements that work in provides essential structural support, with components
concert to regulate its selective permeability (Figure 4). The such as collagen and laminin contributing to the BBB’s
BBB regulates the brain’s internal environment by selective selective permeability and overall stability. Together, these
permeability, allowing small, lipophilic molecules, such as elements form a highly regulated barrier that is crucial for
oxygen and carbon dioxide, to pass freely while restricting brain homeostasis.
larger or charged molecules unless they are actively
transported. This selectivity ensures the controlled entry The BBB is not static; its integrity and function
63
of essential substances, such as glucose, amino acids, and depend on dynamic interactions with surrounding cells.
certain ions. In addition, the BBB serves as a protective The expression and regulation of TJ proteins are crucial
21
barrier against neurotoxins and pathogens through its for maintaining BBB integrity. Pericytes help modulate
efflux transporters, effectively acting as both a physical and the stability and permeability of the BBB by influencing
metabolic shield for the brain. 64 the contractility of ECs and controlling the passage of
macromolecules. Astrocytes release signals that strengthen
ECs of the cerebral capillaries are the core structural ECs’ barriers, while pericytes regulate the expression of
component of the BBB. Unlike peripheral ECs, those in the molecules essential for maintaining BBB properties. ECs
65
brain are connected by TJs and comprised transmembrane can adjust their permeability in response to the brain’s
proteins such as claudins, occludins, and junctional metabolic changes, highlighting the complex and adaptive
adhesion molecules that prevent paracellular transport, 66
making the barrier highly selective. These cells also exhibit nature of BBB maintenance.
minimal transcytosis, further restricting the passage of The BBB is fundamental to proper brain function. By
unwanted substances. Pericytes, embedded within the restricting the entry of toxins, pathogens, and immune cells,
Figure 4. The structure and function of blood–brain barriers and neurovascular unit. Image created using BioRender.com.
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2025) 6 doi: 10.36922/or.8162