Page 54 - OR-1-2
P. 54
A
B
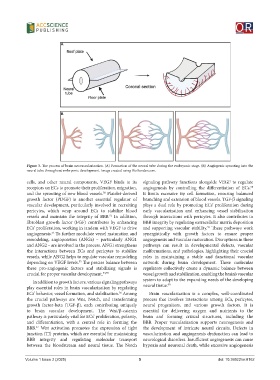
Figure 3. The process of brain neovascularization. (A) Formation of the neural tube during the embryonic stage. (B) Angiogenic sprouting into the
neural tube throughout embryonic development. Image created using BioRender.com.
cells, and other neural components, VEGF binds to its signaling pathway functions alongside VEGF to regulate
receptors on ECs to promote their proliferation, migration, angiogenesis by controlling the differentiation of ECs.
58
50
and the sprouting of new blood vessels. Platelet-derived It limits excessive tip cell formation, ensuring balanced
growth factor (PDGF) is another essential regulator of branching and extension of blood vessels. TGF-β signaling
vascular development, particularly involved in recruiting plays a dual role by promoting ECs’ proliferation during
pericytes, which wrap around ECs to stabilize blood early vascularization and enhancing vessel stabilization
vessels and maintain the integrity of BBB. In addition, through interactions with pericytes. It also contributes to
51
fibroblast growth factor (FGF) contributes by enhancing BBB integrity by regulating extracellular matrix deposition
ECs’ proliferation, working in tandem with VEGF to drive and supporting vascular stability. These pathways work
59
angiogenesis. To further modulate vessel maturation and synergistically with growth factors to ensure proper
52
remodeling, angiopoietins (ANGs) – particularly ANG1 angiogenesis and vascular maturation. Disruptions in these
and ANG2 – are involved in the process. ANG1 strengthens pathways can result in developmental defects, vascular
the interactions between ECs and pericytes to stabilize malformations, and pathologies, highlighting their crucial
vessels, while ANG2 helps to regulate vascular remodeling roles in maintaining a stable and functional vascular
depending on VEGF levels. The precise balance between network during brain development. These molecular
53
these pro-angiogenic factors and stabilizing signals is regulators collectively create a dynamic balance between
crucial for proper vascular development. 54,55 vessel growth and stabilization, enabling the brain’s vascular
In addition to growth factors, various signaling pathways system to adapt to the expanding needs of the developing
60
play essential roles in brain vascularization by regulating neural tissue.
ECs’ behavior, vessel formation, and stabilization. Among Brain vascularization is a complex, well-coordinated
56
the crucial pathways are Wnt, Notch, and transforming process that involves interactions among ECs, pericytes,
growth factor-beta (TGF-β), each contributing uniquely neural progenitors, and various growth factors. It is
to brain vascular development. The Wnt/β-catenin essential for delivering oxygen and nutrients to the
pathway is particularly vital for ECs’ proliferation, polarity, brain and forming critical structures, including the
and differentiation, with a central role in forming the BBB. Proper vascularization supports neurogenesis and
BBB. Wnt activation promotes the expression of tight the development of intricate neural circuits. Defects in
57
junction (TJ) proteins, which are essential for maintaining vascularization and angiogenesis dysfunction can lead to
BBB integrity and regulating molecular transport neurological disorders. Insufficient angiogenesis can cause
between the bloodstream and neural tissue. The Notch hypoxia and neuronal death, while excessive angiogenesis
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2025) 5 doi: 10.36922/or.8162