Page 57 - OR-1-2
P. 57
A B
C D
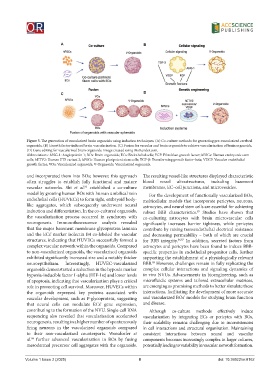
Figure 5. The generation of vascularized brain organoids using induction techniques. (A) Co-culture methods for generating pre-vascularized cerebral
organoids. (B) Growth factor-induced brain vascularization. (C) Fusion for vascular and brain organoids to achieve vascularization of brain organoids.
(D) Gene editing for vascularized brain organoids. Image created using BioRender.com.
Abbreviations: ANG-1: Angiopoietin 1; BOs: Brain organoids; ECs: Endothelial cells; FGF: Fibroblast growth factor; hESCs: Human embryonic stem
cells; hETV2: Human ETS variant 2; hPSCs: Human pluripotent stem cells; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor-beta; VEGF: Vascular endothelial
growth factor; VOs: Vascularized organoids; V-Organoids: Vascularized organoids.
and incorporated them into BOs; however, this approach The resulting vessel-like structures displayed characteristic
often struggles to establish fully functional and mature blood vessel ultrastructures, including basement
vascular networks. Shi et al. established a co-culture membranes, EC–cell junctions, and microvesicles.
83
model by growing human BOs with human umbilical vein For the development of functionally vascularized BOs,
endothelial cells (HUVECs) to form tight, embryoid body- multicellular models that incorporate pericytes, neurons,
like aggregates, which subsequently underwent neural astrocytes, and neural stem cells are essential for achieving
induction and differentiation. In the co-cultured organoids, robust BBB characteristics. Studies have shown that
85
the vascularization process occurred in synchrony with co-culturing astrocytes with brain microvascular cells
neurogenesis. Immunofluorescence analysis revealed significantly increases barrier tightness, while pericytes
that the major basement membrane glycoprotein laminin contribute by raising transendothelial electrical resistance
and the ECs’ marker isolectin B4 co-labeled the vascular and decreasing permeability – both of which are crucial
structures, indicating that HUVECs successfully formed a for BBB integrity. 86,87 In addition, secreted factors from
complex vascular network within the organoids. Compared astrocytes and pericytes have been found to induce BBB-
to non-vascularized organoids, the vascularized organoids specific properties in endothelial progenitor cells, further
exhibited significantly increased size and a notably thicker supporting the establishment of a physiologically relevant
neuroepithelium. Interestingly, HUVEC-vascularized BBB. However, challenges remain in fully replicating the
88
organoids demonstrated a reduction in the hypoxia marker complex cellular interactions and signaling dynamics of
hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha (HIF-1α) and lower levels in vivo NVUs. Advancements in bioengineering, such as
of apoptosis, indicating that vascularization plays a critical microfluidic systems and tailored extracellular matrices,
role in promoting cell survival. Moreover, HUVECs within are emerging as promising methods to better simulate these
the organoids expressed key proteins associated with interactions, facilitating the development of more accurate
vascular development, such as P-glycoprotein, suggesting and vascularized BOs’ models for studying brain function
that neural cells can modulate ECs’ gene expression, and disease.
contributing to the formation of the NVU. Single-cell RNA Although co-culture methods effectively induce
sequencing also revealed that vascularization accelerated vascularization by integrating ECs or pericytes with BOs,
neurogenesis, resulting in a higher number of spontaneously their scalability remains challenging due to inconsistencies
firing neurons in the vascularized organoids compared in cell interactions and structural organization. Maintaining
to their non-vascularized counterparts. Worsdorfer et consistent interactions between neural and vascular
al. further advanced vascularization in BOs by fusing components becomes increasingly complex in larger cultures,
84
mesodermal precursor cell aggregates with the organoids. potentially leading to variability in vascular network formation.
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2025) 8 doi: 10.36922/or.8162