Page 100 - OR-1-3
P. 100
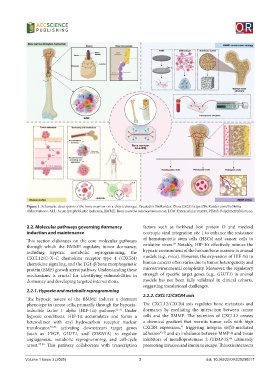
Figure 1. Schematic description of the bone marrow-on-a-chip technique. Created in BioRender. Zhou (2025) https://BioRender.com/ho3468u.
Abbreviations: ALL: Acute lymphoblastic leukemia; BMME: Bone marrow microenvironment; ECM: Extracellular matrix; PDMS: Polydimethylsiloxane.
2.2. Molecular pathways governing dormancy factors such as forkhead box protein O and myeloid
induction and maintenance ecotropic viral integration site 1 to enhance the resistance
This section elaborates on the core molecular pathways of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) and cancer cells to
38
through which the BMME regulates tumor dormancy, oxidative stress. Notably, HIF-1α effectively mimics the
including hypoxic metabolic reprogramming, the hypoxic environment of the human bone marrow in animal
CXCL12/C–X–C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4) models (e.g., mice). However, the expression of HIF-1α in
chemokine signaling, and the TGF-β/bone morphogenetic human cancers often varies due to tumor heterogeneity and
protein (BMP) growth arrest pathway. Understanding these microenvironmental complexity. Moreover, the regulatory
mechanisms is crucial for identifying vulnerabilities in strength of specific target genes (e.g., GLUT1) in animal
dormancy and developing targeted interventions. models has not been fully validated in clinical cohorts,
suggesting translational challenges.
2.2.1. Hypoxia and metabolic reprogramming
2.2.2. CXCL12/CXCR4 axis
The hypoxic nature of the BMME induces a dormant
phenotype in tumor cells, primarily through the hypoxia- The CXCL12/CXCR4 axis regulates bone metastasis and
inducible factor 1 alpha (HIF-1α) pathway. 31-33 Under dormancy by mediating the interaction between tumor
hypoxic conditions, HIF-1α accumulates and forms a cells and the BMME. The secretion of CXCL12 creates
heterodimer with aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear a chemical gradient that recruits tumor cells with high
translocator, 34-36 activating downstream target genes CXCR4 expression, triggering integrin αvβ3-mediated
41
(such as VEGF, GLUT1, and CDKN1A) to regulate adhesion 42,43 and an imbalance between MMP-9 and tissue
44
angiogenesis, metabolic reprogramming, and cell-cycle inhibitors of metalloproteinase 2 (TIMP-2), ultimately
arrest. 37-40 This pathway collaborates with transcription promoting invasion and immune escape. This axis intersects
Volume 1 Issue 3 (2025) 3 doi: 10.36922/OR025200017