Page 101 - OR-1-3
P. 101
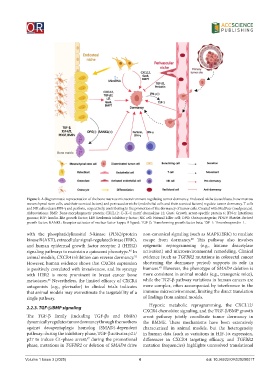
Figure 2. A diagrammatic representation of the bone marrow microenvironment regulating tumor dormancy. Endosteal niche (osteoblasts, bone marrow
mesenchymal stem cells, and their secreted factors) and perivascular niche (endothelial cells and their secreted factors) regulate tumor dormancy. T cells
and NK cells release IFN-γ and perforin, respectively, contributing to the promotion of the dormancy of tumor cells. Created with MedPeer (medpeer.cn).
Abbreviations: BMP: Bone morphogenetic protein; CXCL12: C–X–C motif chemokine 12; Gas6: Growth arrest-specific protein 6; IFN-γ: Interferon
gamma; IGF: Insulin-like growth factor; LIF: Leukemia inhibitory factor; NK cell: Natural killer cell; OPG: Osteoprotegerin; PDGF: Platelet-derived
growth factor; RANKL: Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor beta; TSP-1: Thrombospondin-1.
with the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein non-canonical signaling (such as MAPK/ERK) to mediate
kinase B (AKT), extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), escape from dormancy. This pathway also involves
48
and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) epigenetic reprogramming (e.g., histone deacetylase
signaling pathways to maintain a quiescent phenotype. In activation) and microenvironmental remodeling. Clinical
45
animal models, CXCR4 inhibition can reverse dormancy. evidence (such as TGFBR2 mutations in colorectal cancer
32
However, human evidence shows that CXCR4 expression shortening the dormancy period) supports its role in
48
is positively correlated with invasiveness, and its synergy humans. However, the phenotype of SMAD4 deletion is
with HER2 is more prominent in breast cancer bone more consistent in animal models (e.g., transgenic mice),
metastases. Nevertheless, the limited efficacy of CXCR4 while the TGF-β pathway variations in human cancers are
46
antagonists (e.g., plerixafor) in clinical trials indicates more complex, often accompanied by interference in the
that animal models may overestimate the targetability of a immune microenvironment, limiting the direct translation
single pathway. of findings from animal models.
Hypoxic metabolic reprogramming, the CXCL12/
2.2.3. TGF-β/BMP signaling
CXCR4 chemokine signaling, and the TGF-β/BMP growth
The TGF-β family (including TGF-βs and BMPs) arrest pathway jointly coordinate tumor dormancy in
dynamically regulates tumor dormancy through the mothers the BMME. These mechanisms have been extensively
against decapentaplegic homolog (SMAD)-dependent characterized in animal models, but the heterogeneity
pathway: during the inhibitory phase, TGF-β activates p21/ in human data (such as variations in HIF-1α expression,
p27 to induce G1-phase arrest; during the promotional differences in CXCR4 targeting efficacy, and TGFBR2
47
phase, mutations in TGFBR2 or deletion of SMAD4 drive mutation frequencies) highlights unresolved translational
Volume 1 Issue 3 (2025) 4 doi: 10.36922/OR025200017