Page 44 - OR-1-3
P. 44
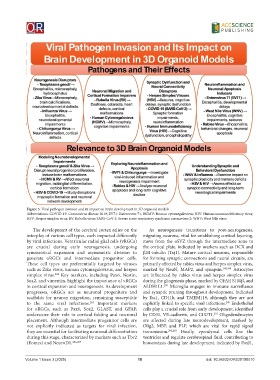
Figure 5. Viral pathogen invasion and its impact on brain development in 3D organoid models
Abbreviations: COVID-19: Coronavirus disease 2019; EV71: Enterovirus 71; HCMV: Human cytomegalovirus; HIV: Human immunodeficiency virus;
HSV: Herpes simplex virus; RV: Rubella virus; SARS-CoV-2: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; WNV: West Nile virus.
The development of the cerebral cortex relies on the As neurogenesis transitions to post-neurogenesis,
interplay of various cell types, each impacted differently migrating neurons, vital for establishing cortical layering,
by viral infections. Ventricular radial glial cells (vRGCs) move from the oSVZ through the intermediate zone to
are crucial during early neurogenesis, undergoing the cortical plate, indicated by markers such as DCX and
symmetrical expansion and asymmetric division to βIII-tubulin (Tuj1). Mature cortical neurons, responsible
generate oRGCs and intermediate progenitor cells. for forming synaptic connections and neural circuits, are
These cell types are preferentially targeted by viruses primarily affected by rabies virus and herpes simplex virus,
such as Zika virus, human cytomegalovirus, and herpes marked by NeuN, MAP2, and synapsin. 288,289 Astrocytes
simplex virus. Key markers, including Pax6, Nestin, are influenced by rabies virus and herpes simplex virus
284
Sox2, and vimentin, highlight the importance of vRGCs during the gliogenesis phase, marked by GFAP, S100β, and
in cortical expansion and neurogenesis. As development ALDH1L1. Microglia engages in immune surveillance
289
progresses, oRGCs act as neuronal progenitors and and synaptic pruning throughout development, indicated
scaffolds for neuron migration, remaining susceptible by Iba1, CD11b, and TMEM119, although they are not
to the same viral infections. Important markers explicitly linked to specific viral infections. Endothelial
285
290
for oRGCs, such as Pax6, Sox2, GLAST, and GFAP, cells play a crucial role from early development, identified
underscore their role in cortical folding and neuronal by CD31, VE-cadherin, and GLUT1. Oligodendrocytes
291
placement. Although intermediate progenitor cells are are affected during late neurodevelopment, marked by
not explicitly indicated as targets for viral infection, Olig2, MBP, and PLP, which are vital for rapid signal
they are essential for facilitating neuronal differentiation transmission. 292,293 Finally, ependymal cells line the
during this stage, characterized by markers such as Tbr2 ventricles and regulate cerebrospinal fluid, contributing to
(Eomes) and NeuroD1. 286,287 homeostasis during late development, indicated by FoxJ1,
Volume 1 Issue 3 (2025) 18 doi: 10.36922/OR025100010